Rocket Fuel In Her Blood: The Story Of JoAnn Morgan
Rocket Fuel in Her Blood: The Story of JoAnn Morgan
As the Apollo 11 mission lifted off on the Saturn V rocket, propelling humanity to the surface of the Moon for the very first time, members of the team inside Launch Control Center watched through a window.
The room was crowded with men in white shirts and dark ties, watching attentively as the rocket thrust into the sky. But among them sat one woman, seated to the left of center in the third row in the image below. In fact, this was the only woman in the launch firing room for the Apollo 11 liftoff.

This is JoAnn Morgan, the instrumentation controller for Apollo 11. Today, this is what Morgan is most known for. But her career at NASA spanned over 45 years, and she continued to break ceiling after ceiling for women involved with the space program.
“It was just meant to be for me to be in the launching business,” she says. “I’ve got rocket fuel in my blood.”

Morgan was inspired to join the human spaceflight program when Explorer 1 was launched into space in 1958, the first satellite to do so from the United States. Explorer 1 was instrumental in discovering what has become known as the Van Allen radiation belt.
“I thought to myself, this is profound knowledge that concerns everyone on our planet,” she says. “This is an important discovery, and I want to be a part of this team. I was compelled to do it because of the new knowledge, the opportunity for new knowledge.”

The opportunity came when Morgan spotted an advertisement for two open positions with the Army Ballistic Missile Agency. The ad listed two Engineer’s Aide positions available for two students over the summer.
“Thank God it said ‘students’ and not ‘boys’” says Morgan, “otherwise I wouldn’t have applied.”
After Morgan got the position, the program was quickly rolled into a brand-new space exploration agency called NASA. Dr. Kurt Debus, the first director of Kennedy Space Center (KSC), looked at Morgan’s coursework and provided Morgan with a pathway to certification. She was later certified as a Measurement and Instrumentation Engineer and a Data Systems Engineer.

There was a seemingly infinite amount of obstacles that Morgan was forced to overcome — everything from obscene phone calls at her station to needing a security guard to clear out the men’s only restroom.
“You have to realize that everywhere I went — if I went to a procedure review, if I went to a post-test critique, almost every single part of my daily work — I’d be the only woman in the room,” reflects Morgan. “I had a sense of loneliness in a way, but on the other side of that coin, I wanted to do the best job I could.”

To be the instrumentation controller in the launch room for the Apollo 11 liftoff was as huge as a deal as it sounds. For Morgan, to be present at that pivotal point in history was ground-breaking: “It was very validating. It absolutely made my career.”

Much like the Saturn V rocket, Morgan’s career took off. She was the first NASA woman to win a Sloan Fellowship, which she used to earn a Master of Science degree in management from Stanford University in California. When she returned to NASA, she became a divisions chief of the Computer Systems division.

From there, Morgan excelled in many other roles, including deputy of Expendable Launch Vehicles, director of Payload Projects Management and director of Safety and Mission Assurance. She was one of the last two people who verified the space shuttle was ready to launch and the first woman at KSC to serve in an executive position, associate director of the center.

To this day, Morgan is still one of the most decorated women at KSC. Her numerous awards and recognitions include an achievement award for her work during the activation of Apollo Launch Complex 39, four exceptional service medals and two outstanding leadership medals. In 1995, she was inducted into the Florida Women's Hall of Fame.
After serving as the director of External Relations and Business Development, she retired from NASA in August 2003.

Today, people are reflecting on the 50th anniversary of Apollo 11, looking back on photos of the only woman in the launch firing room and remembering Morgan as an emblem of inspiration for women in STEM. However, Morgan’s takeaway message is to not look at those photos in admiration, but in determination to see those photos “depart from our culture.”
“I look at that picture of the firing room where I’m the only woman. And I hope all the pictures now that show people working on the missions to the Moon and onto Mars, in rooms like Mission Control or Launch Control or wherever — that there will always be several women. I hope that photos like the ones I’m in don’t exist anymore.”

Follow Women@NASA for more stories like this one, and make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
More Posts from Nasa and Others
Exploring an Asteroid Without Leaving Earth
This 45 day mission – which begins Feb. 1, 2018 – will help our researchers learn how isolation and close quarters affect individual and group behavior. This study at our Johnson Space Center prepares us for long duration space missions, like a trip to an asteroid or even to Mars.

The Human Research Exploration Analog (HERA) that the crew members will be living in is one compact, science-making house. But unlike in a normal house, these inhabitants won’t go outside for 45 days. Their communication with the rest of planet Earth will also be very limited, and they won’t have any access to internet. So no checking social media, kids!
The only people they will talk with regularly are mission control and each other.

The HERA XVI crew is made up of 2 men and 2 women, selected from the Johnson Space Center Test Subject Screening (TSS) pool. The crew member selection process is based on a number of criteria, including criteria similar to what is used for astronaut selection. The four would-be astronauts are:
Kent Kalogera
Jennifer Yen
Erin Hayward
Gregory Sachs
What will they be doing?
The crew are going on a simulated journey to an asteroid, a 715-day journey that we compress into 45 days. They will fly their simulated exploration vehicle around the asteroid once they arrive, conducting several site surveys before 2 of the crew members will participate in a series of virtual reality spacewalks.

They will also be participating in a suite of research investigations and will also engage in a wide range of operational and science activities, such as growing and analyzing plants and brine shrimp, maintaining and “operating” an important life support system, exercising on a stationary bicycle or using free weights, and sharpening their skills with a robotic arm simulation.

During the whole mission, they will consume food produced by the Johnson Space Center Food Lab – the same food that the astronauts enjoy on the International Space Station – which means that it needs to be rehydrated or warmed in a warming oven.
This simulation means that even when communicating with mission control, there will be a delay on all communications ranging from 1 to 5 minutes each way.
A few other details:
The crew follows a timeline that is similar to one used for the space station crew.
They work 16 hours a day, Monday through Friday. This includes time for daily planning, conferences, meals and exercise.
Mission: February 1, 2018 - March 19, 2018

But beware! While we do all we can to avoid crises during missions, crews need to be able to respond in the event of an emergency. The HERA crew will conduct a couple of emergency scenario simulations, including one that will require them to respond to a decrease in cabin pressure, potentially finding and repairing a leak in their spacecraft.
Throughout the mission, researchers will gather information about living in confinement, teamwork, team cohesion, mood, performance and overall well-being. The crew members will be tracked by numerous devices that each capture different types of data.
Learn more about the HERA mission HERE.
Explore the HERA habitat via 360-degree videos HERE.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Tune in, Starliner! How NASA’s Near Space Network Powers Communications

On May 19, 2022, our partners at Boeing launched their Starliner CST-100 spacecraft to the International Space Station as a part of our Commercial Crew Program. This latest test puts the company one step closer to joining the SpaceX Crew Dragon in ferrying astronauts to and from the orbiting laboratory. We livestreamed the launch and docking at the International Space Station, but how? Let’s look at the communications and navigation infrastructure that makes these missions possible.

Primary voice and data communications are handled by our constellation of Tracking and Data Relay Satellites (TDRS), part of our Near Space Network. These spacecraft relay communications between the crewed vehicles and mission controllers across the country via terrestrial connections with TDRS ground stations in Las Cruces, New Mexico, and Guam, a U.S. territory in the Pacific Ocean.
TDRS, as the primary communications provider for the space station, is central to the services provided to Commercial Crew vehicles. All spacecraft visiting the orbiting laboratory need TDRS services to successfully complete their missions.

During launches, human spaceflight mission managers ensure that Commercial Crew missions receive all the TDRS services they need from the Near Space Operations Control Center at our Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. There, communications engineers synthesize network components into comprehensive and seamless services for spacecraft as they launch, dock, undock, and deorbit from the space station.

Nearby, at our Flight Dynamics Facility, navigation engineers track the spacecraft on their ascent, leveraging years of experience supporting the navigation needs of crewed missions. Using tracking data sent to our Johnson Space Center in Houston and relayed to Goddard, these engineers ensure astronaut safety throughout the vehicles’ journey to the space station.
Additionally, our Search and Rescue office monitors emergency beacons on Commercial Crew vehicles from their lab at Goddard. In the unlikely event of a launch abort, the international satellite-aided search and rescue network will be able to track and locate these beacons, helping rescue professionals to return the astronauts safely. For this specific uncrewed mission, the search and rescue system onboard the Boeing Starliner will not be activated until after landing for ground testing.

To learn more about NASA’s Space Communications and Navigation (SCaN) services and technologies, visit https://www.nasa.gov/directorates/heo/scan/index.html. To learn more about NASA’s Near Space Network, visit https://esc.gsfc.nasa.gov/projects/NSN.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space!
Earth’s Hot and It’s Cold 🎶(and We Can Tell from Space)
From people and pets to pens and pencils, everything gives off energy in the form of heat. We’ve got special instruments that measure thermal wavelengths, so we can tell whether something is hot, cold or in between. Hotter things emit more thermal energy; colder ones emit less.

We have special instruments in space, zipping around Earth and measuring the hottest and coldest places on our planet.

We can also measure much subtler changes in heat – like when plants cool down as they take up water from the soil and ‘sweat’ it out into the air, in a process called evapotranspiration.

This lets us identify healthy, growing crops around the world.

The instrument that can do all this is called the Thermal Infrared Sensor 2 (TIRS-2). It just passed a series of rigorous tests at our Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Md., proving it’s ready to survive in space.

TIRS-2 is bound for the Landsat 9 satellite, which will continue decades of work studying our planet from space.

Learn more about TIRS-2 and how we see heat from space: https://www.nasa.gov/feature/goddard/2019/new-landsat-infrared-instrument-ships-from-nasa/.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
Solar System: 5 Things To Know This Week
Our solar system is huge, so let us break it down for you. Here are 5 things to know this week:
1. Dancing with a Star

Our local star, better known as the sun, teems with activity. This month NASA has been tracking regions that burst with magnetic loops. The Solar Dynamics Observatory is one of several space-based assets that keep tabs on the sun daily, watching as charged particles trace the magnetic field, forming bright lines as they emit light in ultraviolet wavelengths.
2. An Idyll for Ida

On Nov. 24, the asteroid Ida makes its closest approach to Earth (at a very safe distance). Ida is the first asteroid found to have its own moon, and the second ever visited by a spacecraft. Its close encounter happened in 1993 as Galileo flew by en route to Jupiter.
3. Moonshine

On Nov. 23, the Cassini spacecraft will fly near Saturn's icy moon Tethys. Several instruments aboard Cassini will collect data, including an eight-frame color image mosaic. Between Nov. 27 and Dec. 2, Cassini will have very limited communications with Earth, because Cassini will enter solar conjunction, when Cassini and Saturn are on the other side of the Sun from Earth.
4. The Moon Will Occult Aldebaran

That may sound ominous, but all it means is that Earth's moon will pass in front of the giant red star Aldebaran on Nov. 26. Aldebaran is the bright "eye" of the constellation Taurus. The event will only be visible in some parts of North America. Details can be found HERE.
5. One Wild Ride, One Year Later

What a year it's been for the Rosetta mission since the Philae lander came to rest on the surface of Comet 67P/Churyumov-Gerasimenko in November 2014. A steady flow of data from the orbiter, together with several days of information sent from the lander, is providing a detailed picture of this remnant from the creation of the solar system.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
100th Anniversary of Einstein’s Theory of Relativity
One hundred years ago this month, Albert Einstein published his theory of general relativity (GR), one of the most important scientific achievements in the last century.

A key result of Einstein’s theory is that matter warps space-time, and thus a massive object can cause an observable bending of light from a background object. The first success of the theory was the observation, during a solar eclipse, that light from a distant background star was deflected by the predicted amount as it passed near the sun.
When Einstein developed the general theory of relativity, he was trying to improve our understanding of how the universe works. At the time, Newtonian gravity was more than sufficient for any practical gravity calculations. However, as often happens in physics, general relativity has applications that would not have been foreseen by Einstein or his contemporaries.

How many of us have used a smartphone to get directions? Or to tag our location on social media? Or to find a recommendation for a nearby restaurant? These activities depend on GPS. GPS uses radio signals from a network of satellites orbiting Earth at an altitude of 20,000 km to pinpoint the location of a GPS receiver. The accuracy of GPS positioning depends on precision in time measurements of billionths of a second. To achieve such timing precision, however, relativity must be taken into account.
Our Gravity Probe B (GP-B) mission has confirmed two key predictions derived from Albert Einstein's general theory of relativity, which the spacecraft was designed to test. The experiment, launched in 2004, and measured the warping of space and time around a gravitational body, and frame-dragging, the amount a spinning object pulls space and time with it as it rotates.
Scientists continue to look for cracks in the theory, testing general relativity predictions using laboratory experiments and astronomical observations. For the past century, Einstein’s theory of gravity has passed every hurdle.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
What Science is Launching to Space?

The tenth SpaceX cargo resupply mission launched to the International Space Station on Feb. 18, and is carrying science ranging from protein crystal growth studies to Earth science payloads. Here’s a rundown of some of the highlights heading to the orbiting laboratory.

The CASIS PCG 5 investigation will crystallize a human monoclonal antibody, developed by Merck Research Labs, that is currently undergoing clinical trials for the treatment of immunological disease. Results from this investigation have the potential to improve the way monoclonal antibody treatments are administered on Earth.

Without proteins, the human body would be unable to repair, regulate or protect itself. Crystallizing proteins provides better views of their structure, which helps scientists to better understand how they function. Often times, proteins crystallized in microgravity are of higher quality than those crystallized on Earth. LMM Biophysics 1 explores that phenomena by examining the movement of single protein molecules in microgravity. Once scientists understand how these proteins function, they can be used to design new drugs that interact with the protein in specific ways and fight disease.

Much like LMM Biophysics 1, LMM Biophysics 3 aims to use crystallography to examine molecules that are too small to be seen under a microscope, in order to best predict what types of drugs will interact best with certain kinds of proteins. LMM Biophysics 3 will look specifically into which types of crystals thrive and benefit from growth in microgravity, where Earth’s gravity won’t interfere with their formation. Currently, the success rate is poor for crystals grown even in the best of laboratories. High quality, space-grown crystals could improve research for a wide range of diseases, as well as microgravity-related problems such as radiation damage, bone loss and muscle atrophy.


Nanobiosym Predictive Pathogen Mutation Study (Nanobiosym Genes) will analyze two strains of bacterial mutations aboard the station, providing data that may be helpful in refining models of drug resistance and support the development of better medicines to counteract the resistant strains.

During the Microgravity Expanded Stem Cells investigation, crew members will observe cell growth and morphological characteristics in microgravity and analyze gene expression profiles of cells grown on the station. This information will provide insight into how human cancers start and spread, which aids in the development of prevention and treatment plans. Results from this investigation could lead to the treatment of disease and injury in space, as well as provide a way to improve stem cell production for human therapy on Earth.

The Lightning Imaging Sensor will measure the amount, rate and energy of lightning as it strikes around the world. Understanding the processes that cause lightning and the connections between lightning and subsequent severe weather events is a key to improving weather predictions and saving life and property.

From the vantage of the station, the LIS instrument will sample lightning over a wider geographical area than any previous sensor.

Future robotic spacecraft will need advanced autopilot systems to help them safely navigate and rendezvous with other objects, as they will be operating thousands of miles from Earth.

The Raven (STP-H5 Raven) studies a real-time spacecraft navigation system that provides the eyes and intelligence to see a target and steer toward it safely. Research from Raven can be applied toward unmanned vehicles both on Earth and in space, including potential use for systems in NASA’s future human deep space exploration.

SAGE III will measure stratospheric ozone, aerosols, and other trace gases by locking onto the sun or moon and scanning a thin profile of Earth’s atmosphere.

These measurements will allow national and international leaders to make informed policy decisions regarding the protection and preservation of Earth’s ozone layer. Ozone in the atmosphere protects Earth’s inhabitants, including humans, plants and animals, from harmful radiation from the sun, which can cause long-term problems such as cataracts, cancer and reduced crop yield.

Tissue Regeneration-Bone Defect (Rodent Research-4) a U.S. National Laboratory investigation sponsored by the Center for the Advancement of Science in Space (CASIS) and the U.S. Army Medical Research and Materiel Command, studies what prevents other vertebrates such as rodents and humans from re-growing lost bone and tissue, and how microgravity conditions impact the process.

Results will provide a new understanding of the biological reasons behind a human’s inability to grow a lost limb at the wound site, and could lead to new treatment options for the more than 30% of the patient.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Solar System: 10 Things to Know This Week
Need some space?
Here are 10 perspective-building images for your computer desktop and mobile device wallpaper.
These are all real images, sent very recently by our planetary missions throughout the solar system.
1. Our Sun

Warm up with this view from our Solar Dynamics Observatory showing active regions on the Sun in October 2017. They were observed in a wavelength of extreme ultraviolet light that reveals plasma heated to over a million degrees.
Downloads Desktop: 1280 x 800 | 1600 x 1200 | 1920 x 1200 Mobile: 1440 x 2560 | 1080 x 1920 | 750 x 1334
2. Jupiter Up-Close

This series of enhanced-color images shows Jupiter up close and personal, as our Juno spacecraft performed its eighth flyby of the gas giant planet on Sept. 1, 2017.
Downloads Desktop: 1280 x 800 | 1600 x 1200 | 1920 x 1200 Mobile: 1440 x 2560 | 1080 x 1920 | 750 x 1334
3. Saturn’s and Its Rings

With this mosaic from Oct. 28, 2016, our Cassini spacecraft captured one of its last looks at Saturn and its main rings from a distance.
Downloads Desktop: 1280 x 800 | 1600 x 1200 | 1920 x 1200 Mobile: 1440 x 2560 | 1080 x 1920 | 750 x 1334
4. Gale Crater on Mars

This look from our Curiosity Mars rover includes several geological layers in Gale crater to be examined by the mission, as well as the higher reaches of Mount Sharp beyond. The redder rocks of the foreground are part of the Murray formation. Pale gray rocks in the middle distance of the right half of the image are in the Clay Unit. A band between those terrains is "Vera Rubin Ridge," where the rover is working currently. The view combines six images taken with the rover's Mast Camera (Mastcam) on Jan. 24, 2017.
Downloads Desktop: 1280 x 800 | 1600 x 1200 | 1920 x 1200 Mobile: 1440 x 2560 | 1080 x 1920 | 750 x 1334
5. Sliver of Saturn

Cassini peers toward a sliver of Saturn's sunlit atmosphere while the icy rings stretch across the foreground as a dark band on March 31, 2017. This view looks toward the unilluminated side of the rings from about 7 degrees below the ring plane.
Downloads Desktop: 1280 x 800 | 1600 x 1200 | 1920 x 1200 Mobile: 1440 x 2560 | 1080 x 1920 | 750 x 1334
6. Dwarf Planet Ceres

This image of the limb of dwarf planet Ceres shows a section of the northern hemisphere, as seen by our Dawn mission. Prominently featured is Occator Crater, home of Ceres' intriguing "bright spots." The latest research suggests that the bright material in this crater is comprised of salts left behind after a briny liquid emerged from below.
Downloads Desktop: 1280 x 800 | 1600 x 1200 | 1920 x 1200 Mobile: 1440 x 2560 | 1080 x 1920 | 750 x 1334
7. Martian Crater

This image from our Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) shows a crater in the region with the most impressive known gully activity in Mars' northern hemisphere. Gullies are active in the winter due to carbon dioxide frost, but northern winters are shorter and warmer than southern winters, so there is less frost and less gully activity.
Downloads Desktop: 1280 x 800 | 1600 x 1200 | 1920 x 1200 Mobile: 1440 x 2560 | 1080 x 1920 | 750 x 1334
8. Dynamic Storm on Jupiter

A dynamic storm at the southern edge of Jupiter's northern polar region dominates this Jovian cloudscape, courtesy of Juno. This storm is a long-lived anticyclonic oval named North North Temperate Little Red Spot 1. Citizen scientists Gerald Eichstädt and Seán Doran processed this image using data from the JunoCam imager.
Downloads Desktop: 1280 x 800 | 1600 x 1200 | 1920 x 1200 Mobile: 1440 x 2560 | 1080 x 1920 | 750 x 1334
9. Rings Beyond Saturn’s Sunlit Horizon

This false-color view from the Cassini spacecraft gazes toward the rings beyond Saturn's sunlit horizon. Along the limb (the planet's edge) at left can be seen a thin, detached haze.
Downloads Desktop: 1280 x 800 | 1600 x 1200 | 1920 x 1200 Mobile: 1440 x 2560 | 1080 x 1920 | 750 x 1334
10. Saturn’s Ocean-Bearing Moon Enceladus

Saturn's active, ocean-bearing moon Enceladus sinks behind the giant planet in a farewell portrait from Cassini. This view of Enceladus was taken by NASA's Cassini spacecraft on Sept. 13, 2017. It is among the last images Cassini sent back before its mission came to an end on Sept. 15, after nearly 20 years in space.
Downloads Desktop: 1280 x 800 | 1600 x 1200 | 1920 x 1200 Mobile: 1440 x 2560 | 1080 x 1920 | 750 x 1334
Applying Wallpaper: 1. Click on the screen resolution you would like to use. 2. Right-click on the image (control-click on a Mac) and select the option 'Set the Background' or 'Set as Wallpaper' (or similar).
Places to look for more of our pictures include solarsystem.nasa.gov/galleries, images.nasa.gov and www.jpl.nasa.gov/spaceimages.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
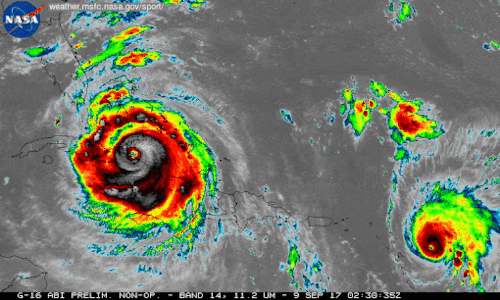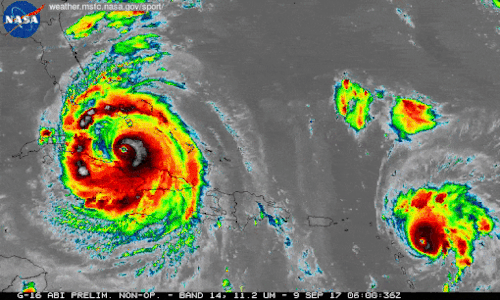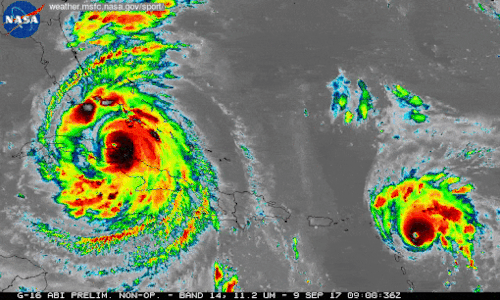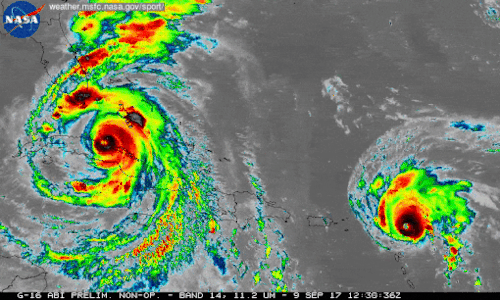
We're using our unique vantage point in space to provide observations and data of Hurricane Irma and other tropical storms. Hurricanes Irma and Jose are seen here in a 12-hour long infrared loop. Scientists monitor storms in infrared to closely monitor clouds and storm intensity. We continue to provide satellite imagery for these storms, tracking its trajectory, force and precipitation to inform forecasters at the National Hurricane Center.
As these storms continue their westward drive in the coming days, they will be passing over waters that are warmer than 30 degrees Celsius (86 degrees Fahrenheit)—hot enough to sustain a category 5 storm. Warm oceans, along with low wind shear, are two key ingredients that fuel and sustain hurricanes. Get the latest imagery and data from us at www.nasa.gov/hurricane For information on making preparations for Hurricanes, visit the FEMA website at: ready.gov/hurricanes. Credit: NASA-SPoRT/NOAA
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
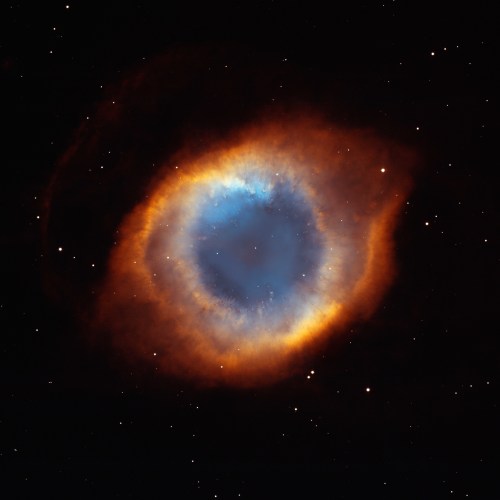
Say hello to the Helix Nebula 👋
In 2001 and 2002, our Hubble Space Telescope looked at the Helix Nebula and it looked right back! This planetary nebula is right in our cosmic neighborhood, only about 650 light-years away. Gigantic for this type of cosmic object, the Helix Nebula stretches across 2 to 3 light-years.
With no actual connection to planets, planetary nebulas like this one are produced when a medium-mass star dies and sloughs off its outer layers. These gaseous layers are expelled into space at astonishing speeds where they light up like fireworks. The Helix Nebula is one of the closest planetary nebulas to Earth, giving scientists an up-close view of its strange affairs.
Through Hubble’s observations, scientists have learned that the Helix Nebula isn’t doughnut-shaped as it appears. Instead it consists of two disks that are nearly perpendicular to each other — the nebula looks like an eye and bulges out like one too!
Hubble has also imaged comet-like tendrils that form a pattern around the central star like the spokes on a wagon wheel, likely resulting from a collision between gases. The dying star spews hot gas from its surface, which crashes into the cooler gas that it ejected 10,000 years before. Eventually the knots will dissipate into the cold blackness of interstellar space.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
Did you have an innate talent for math? Or did you struggle and practiced until you understood it? I wanted to become an aerospace engineer but after taking a class I decided psychology was more suited for me because I struggled with equations but thrived with the psychological terms
Anything you don’t know is hard until you learn it. There are a few geniuses in the world, but most people study and work hard to learn what they love. Even the smartest amongst you actually put in a lot of time to learn the things that they want, and no one is an exception. You have to put in the time.
-
 beyondafinecupofcoffee liked this · 1 year ago
beyondafinecupofcoffee liked this · 1 year ago -
 junsnow liked this · 2 years ago
junsnow liked this · 2 years ago -
 gimmegreen liked this · 2 years ago
gimmegreen liked this · 2 years ago -
 writtenweaponry liked this · 2 years ago
writtenweaponry liked this · 2 years ago -
 stjimmyisdead reblogged this · 3 years ago
stjimmyisdead reblogged this · 3 years ago -
 itl00ksbetterinblack liked this · 3 years ago
itl00ksbetterinblack liked this · 3 years ago -
 zacktastic liked this · 3 years ago
zacktastic liked this · 3 years ago -
 actuarystudying liked this · 3 years ago
actuarystudying liked this · 3 years ago -
 isoboto reblogged this · 4 years ago
isoboto reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 teapoetryx liked this · 4 years ago
teapoetryx liked this · 4 years ago -
 isoboto liked this · 4 years ago
isoboto liked this · 4 years ago -
 sulestarlight liked this · 4 years ago
sulestarlight liked this · 4 years ago -
 justatheatrekidwholovesspace liked this · 4 years ago
justatheatrekidwholovesspace liked this · 4 years ago -
 chelsiegeorgia liked this · 4 years ago
chelsiegeorgia liked this · 4 years ago -
 sbtg-outofcontext liked this · 4 years ago
sbtg-outofcontext liked this · 4 years ago -
 nelmarfan liked this · 4 years ago
nelmarfan liked this · 4 years ago -
 hipstersoulgushers liked this · 4 years ago
hipstersoulgushers liked this · 4 years ago -
 sirmedicknight reblogged this · 4 years ago
sirmedicknight reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 wintercass34 reblogged this · 4 years ago
wintercass34 reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 alialaya liked this · 4 years ago
alialaya liked this · 4 years ago -
 vo-kopen reblogged this · 4 years ago
vo-kopen reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 destructivegremlin reblogged this · 4 years ago
destructivegremlin reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 avengersemhwasp1 reblogged this · 4 years ago
avengersemhwasp1 reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 avengersemhwasp1 liked this · 4 years ago
avengersemhwasp1 liked this · 4 years ago -
 clockpunkgamelover reblogged this · 4 years ago
clockpunkgamelover reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 clockpunkgamelover liked this · 4 years ago
clockpunkgamelover liked this · 4 years ago -
 -psycho- liked this · 4 years ago
-psycho- liked this · 4 years ago -
 cibolasworld liked this · 4 years ago
cibolasworld liked this · 4 years ago -
 svenskadata liked this · 4 years ago
svenskadata liked this · 4 years ago -
 the-prince-of-tides reblogged this · 4 years ago
the-prince-of-tides reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 the-prince-of-tides liked this · 4 years ago
the-prince-of-tides liked this · 4 years ago -
 statmystic reblogged this · 4 years ago
statmystic reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 odn5t9rhpxr7 liked this · 4 years ago
odn5t9rhpxr7 liked this · 4 years ago -
 yaiathings liked this · 4 years ago
yaiathings liked this · 4 years ago -
 lunar425 liked this · 4 years ago
lunar425 liked this · 4 years ago -
 staying-rad liked this · 4 years ago
staying-rad liked this · 4 years ago -
 nameh0arder liked this · 4 years ago
nameh0arder liked this · 4 years ago
Explore the universe and discover our home planet with the official NASA Tumblr account
1K posts