Hello, Scott? It’s President Obama.
Hello, Scott? It’s President Obama.
This afternoon, President Obama spoke by phone with astronaut Scott Kelly to welcome him back to Earth from his record-breaking yearlong mission on the International Space Station.

President Obama, above, is seen talking on the phone with Scott Kelly in the Oval Office on March 2, 2016. (Official White House Photo by Pete Souza)
The President thanked Kelly for his service, for sharing his journey with people across the globe through social media, for his participation in important research about what it will take for us to make long journeys in space, and for inspiring a new generation of young people to pursue studies and careers in science, technology, engineering, and mathematics.

The President also noted that Kelly’s year in space would provide critical data to researchers trying to understand how to keep astronauts healthy during long space voyages and fulfill the President’s vision of putting American astronauts on Mars in the 2030s.
Thanks to Kelly’s work, in addition to that of everyone at NASA and in the U.S. space industry, the President believes the United States will be successful in that journey to Mars and will continue to lead and inspire the world in space exploration.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
More Posts from Nasa and Others
What popular film is the closest to reality for you?
All Eyes on Harvey
Our Earth-observing satellites, along with the cameras and crew of the International Space Station, are keeping a watchful eye over Hurricane Harvey as it churns in the Gulf of Mexico. When Hurricane Harvey blows ashore over coastal Texas on Friday night, it will likely be the first major hurricane to make landfall in the United States since 2005.

Above is a view of Harvey from NOAA's GOES-East satellite captured on Aug. 25 at 10:07 a.m. EDT (1407 UTC) clearly showing the storm’s eye as Harvey nears landfall in the southeastern coast of Texas. As Hurricane Harvey continued to strengthen, we analyzed the storm’s rainfall, cloud heights and cloud top temperatures.

Above, the Global Precipitation Mission (GPM) core observatory satellite flew almost directly above intensifying Hurricane Harvey on August 24, 2017 at 6:30 p.m. EDT (2230 UTC) and we used the Microwave Imager instrument to peer through dense storm clouds to reveal the location of intense rainfall bands near the center of the hurricane.
And from the International Space Station, cameras were pointed towards Harvey as the orbiting laboratory passed overhead 250 miles above the Earth. The video above includes views from the space station recorded on August 24, 2017 at 6:15 p.m. Eastern Time.
The National Hurricane Center expects Harvey to be a category 3 storm on the Saffir-Simpson scale—with winds higher than 111 miles (179 kilometers) per hour—when it makes landfall. It will likely produce a storm surge of 6 to 12 feet (2 to 4 meters) and drop between 15 and 25 inches (38 and 63 centimeters) of rain in some areas—enough to produce life-threatening flash floods.
For updated forecasts, visit the National Hurricane Center. Ensure you are prepared for Hurricanes. Get tips and more at FEMA’s Ready site. Get the latest updates from NASA satellites by visiting our Hurricane site.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Another Station Upgrade:
Spacewalkers Jeff Williams and Kate Rubins to install new TV cameras
On Thursday, Sept. 1, U.S. astronauts Jeff Williams and Kate Rubins will conduct the station’s 195th American spacewalk. As part of their activities, the pair will install the first of several enhanced high-definition television cameras that will monitor activities outside the station, including the comings and goings of visiting cargo and crew vehicles

Working on the station’s backbone, or truss, Williams and Rubins will retract a thermal radiator that is part of the station’s cooling system.

As was the case for their first spacewalk together on Aug. 19, Williams will be designated as extravehicular crew member 1 (EV1), wearing a spacesuit with a red stripe, while Rubins will be EV2, wearing a suit with no stripes.
Watch LIVE!
Coverage of the spacewalk begins at 6:30 a.m. EDT on Thursday, Sept. 1; with the spacewalk scheduled to begin at 8:05 a.m. EDT. Stream live online HERE.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
What’s Up for November 2016
What’s Up for November: Venus at sunset, Jupiter at dawn, your last evening glimpse of Saturn until spring, and more meteors!

Through November 3, catch glimpses of a gibbous Venus, a crescent moon and ringed Saturn in the southwest sky just after sunset.

Wake up before sunrise every day this month to see Jupiter just above Spica, the brightest star in the constellation Virgo, shining in the east-southeast sky.
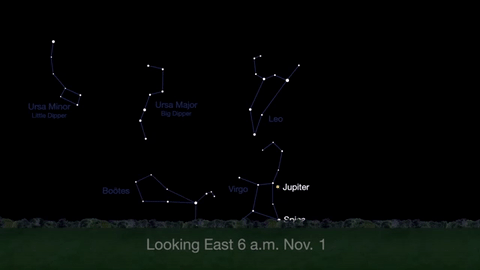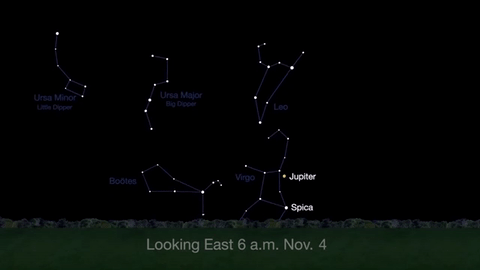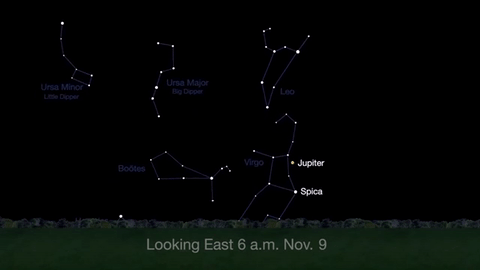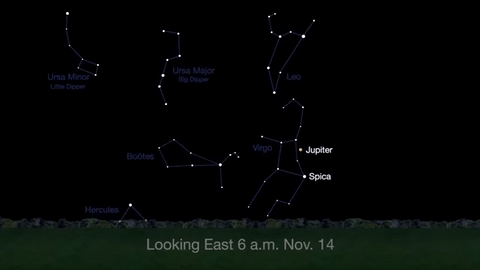
Just before dawn on November 23-24, see the waning crescent moon just above Jupiter.
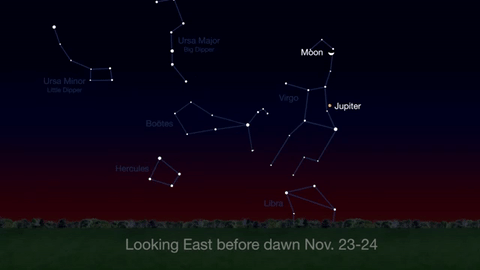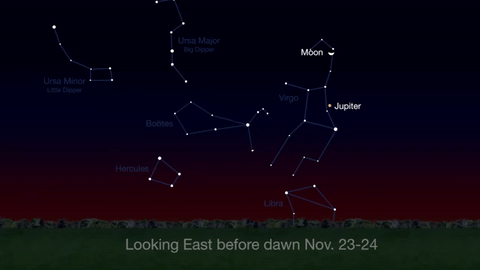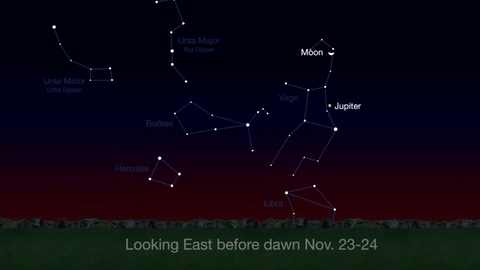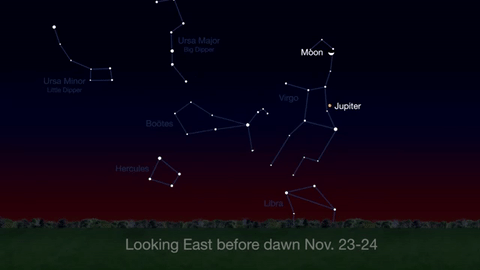
November is a great time to see the constellation Ceres as it glides past Cetus, the Whale and you will be able to see the dwarf planet move relative to the background stars, but you’ll need a telescope for this one.
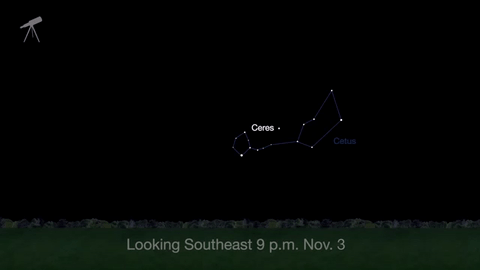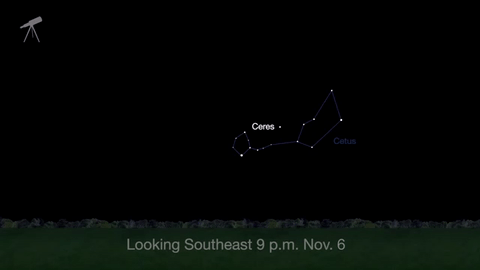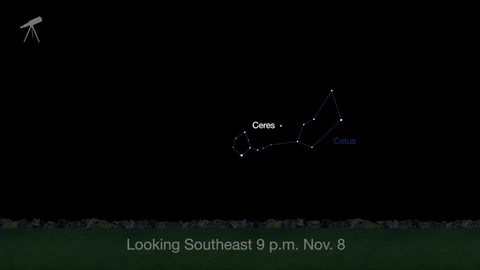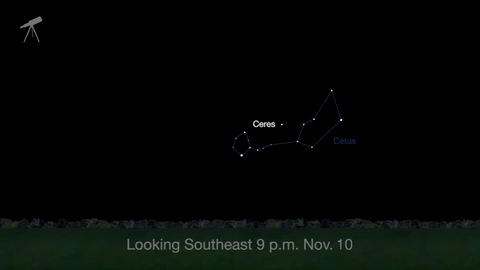
This month, just like last month, there will be three meteor showers--the Northern Tuarids, the Leonids and the November Orionids.

Watch the full November “What’s Up" video for more:
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
What’s Up for June 2017?
Have a planet party and compare Saturn and Jupiter! We’ll show you where and when to point your telescope or binoculars to see these planets and their largest moons.

Meet at midnight to have a planetary party when Jupiter and Saturn are visible at the same time!

The best time will be after midnight on June 17. To see the best details, you’ll need a telescope.

Saturn will be at opposition on June 15, when Saturn, the Earth and the sun are in a straight line.

Opposition provides the best views of Saturn and several of its brightest moons. At the very least, you should be able to see Saturn’s moon Titan, which is larger and brighter than Earth’s moon.

As mentioned earlier, you’ll be able to see Jupiter and Saturn in the night sky this month. Through a telescope, you’ll be able to see the cloud bands on both planets. Saturn’s cloud bands are fainter than those on Jupiter.

You’ll also have a great view of Saturn’s Cassini Division, discovered by astronomer Giovanni Cassini in 1675, namesake of our Cassini spacecraft.

Our Cassini spacecraft has been orbiting the planet since 2004 and is on a trajectory that will ultimately plunge it into Saturn’s atmosphere on September 15, 2017, bringing the mission to a close.

Our Juno spacecraft recently completed its sixth Jupiter flyby. Using only binoculars you can observe Jupiter’s 4 Galilean moons - Io, Callisto, Ganymede and Europa.

To learn about What’s Up in the skies for June 2017, watch the full video:
For more astronomy events, check out NASA's Night Sky Network at https://nightsky.jpl.nasa.gov/.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Studying Sediments in Space
An International Space Station investigation called BCAT-CS studies dynamic forces between sediment particles that cluster together.

For the study, scientists sent mixtures of quartz and clay particles to the space station and subjected them to various levels of simulated gravity.

Conducting the experiment in microgravity makes it possible to separate out different forces that act on sediments and look at the function of each.

Sediment systems of quartz and clay occur many places on Earth, including rivers, lakes, and oceans, and affect many activities, from deep-sea hydrocarbon drilling to carbon sequestration.

Understanding how sediments behave has a range of applications on Earth, including predicting and mitigating erosion, improving water treatment, modeling the carbon cycle, sequestering contaminants and more accurately finding deep sea oil reservoirs.

It also may provide insight for future studies of the geology of new and unexplored planets.

Follow @ISS_RESEARCH to learn more.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
In Case You Missed It...
NASA astronaut Jessica Meir sat down and answered your questions during a Tumblr AnswerTime session!
But don’t worry, we’ve got a recap for you! In addition to the highlights below, you can check out the full AnswerTime here.

Astronaut Jessica Meir was selected as part of our 2013 astronaut class (which was 50% women!) and is currently training to go to space. She could be one of the first astronauts to ride in the Orion spacecraft, which will carry humans deeper into space than ever before.

Let’s check out some of her responses...





Follow astronaut Jessica Meir for more: @Astro_Jessica on Twitter and Instagram and follow the Orion space capsule as it prepares to fly to deep space on Twitter and Facebook. Follow NASA on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Summer Starts in the Northern Hemisphere!
Today is the first day of summer in the Northern Hemisphere -- the solstice! People located in the Northern Hemisphere will have the longest day of the year today, and people located in the Southern Hemisphere will have the shortest day of the year.

The angle between the Earth’s orbit and the axis of its rotation creates our seasons, tilting each hemisphere toward the Sun during summer in that half of the Earth. This is summer in the Northern Hemisphere, and winter in the Southern Hemisphere. The other half of the year, the Northern Hemisphere is tilted away from the Sun, creating winter in the north and summer in the south.

Solstices happen twice per year, at the points in Earth’s orbit where this tilt is most pronounced.

These days are the longest (in the summer hemisphere) and shortest (in the winter hemisphere) of the year, and mark the change of seasons to summer and winter, respectively.
For more Earth science, follow NASA Earth on Twitter, on Facebook, or on the web.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space!
Chandra X-Ray Observatory, We Appreciate You
On July 23, 1999, the Space Shuttle Columbia blasted off from the Kennedy Space Center carrying the Chandra X-ray Observatory. In the two decades that have passed, Chandra’s powerful and unique X-ray eyes have contributed to a revolution in our understanding of the cosmos.

Since its launch 20 years ago, Chandra's unrivaled X-ray vision has changed the way we see the universe.

Chandra has captured galaxy clusters – the largest gravitationally bound objects in the universe – in the process of merging.

Chandra has shown us the powerful wind and shock fronts that rumble through star-forming systems.

And a star school, so to speak -- home to thousands of the Milky Way's biggest and brightest.

Carl Sagan said, "We are made of star-stuff." It's true. Most of the elements necessary for life are forged inside stars and blasted into interstellar space by supernovas. Chandra has tracked them.

Thank you Chandra X-Ray! To more adventures with you!

Check out Chandra’s 20th anniversary page to see how they are celebrating.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.

Say hello to spiral galaxy NGC 1097 👋
About 45 million light-years away, in another corner of the cosmos, lies spiral galaxy NGC 1097. Though this Hubble Space Telescope image zooms in toward the core, the galaxy’s vast spiral arms span over 100,000 light-years as they silently sweep through space. At the heart of this galaxy lurks a black hole that is about 100 million times as massive as the Sun.
The supermassive black hole is voraciously eating up surrounding matter, which forms a doughnut-shaped ring around it. Matter that's pulled into the black hole releases powerful radiation, making the star-filled center of the galaxy even brighter. Hubble’s observations have led to the discovery that while the material that is drawn toward NGC 1097’s black hole may be doomed to die, new stars are bursting into life in the ring around it.
This sparkling spiral galaxy is especially interesting to both professional scientists and amateur astronomers. It is a popular target for supernova hunters ever since the galaxy experienced three supernovas in relatively rapid succession — just over a decade, between 1992 and 2003. Scientists are intrigued by the galaxy’s satellites — smaller “dwarf” galaxies that orbit NGC 1097 like moons. Studying this set of galaxies could reveal new information about how galaxies interact with each other and co-evolve.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
-
 sevendevilsinwesteros liked this · 1 year ago
sevendevilsinwesteros liked this · 1 year ago -
 jsbustaman liked this · 9 years ago
jsbustaman liked this · 9 years ago -
 go-bama reblogged this · 9 years ago
go-bama reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 hybridanafrost liked this · 9 years ago
hybridanafrost liked this · 9 years ago -
 amandathyst reblogged this · 9 years ago
amandathyst reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 lovinggodherself liked this · 9 years ago
lovinggodherself liked this · 9 years ago -
 agentreptile liked this · 9 years ago
agentreptile liked this · 9 years ago -
 bionystone liked this · 9 years ago
bionystone liked this · 9 years ago -
 gregorychatman liked this · 9 years ago
gregorychatman liked this · 9 years ago -
 soapysuddz reblogged this · 9 years ago
soapysuddz reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 bazillas liked this · 9 years ago
bazillas liked this · 9 years ago -
 mcgarrygirl78 reblogged this · 9 years ago
mcgarrygirl78 reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 mcgarrygirl78 liked this · 9 years ago
mcgarrygirl78 liked this · 9 years ago -
 rjbailey reblogged this · 9 years ago
rjbailey reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 rjbailey liked this · 9 years ago
rjbailey liked this · 9 years ago -
 wenrina-blog liked this · 9 years ago
wenrina-blog liked this · 9 years ago -
 ahahlover liked this · 9 years ago
ahahlover liked this · 9 years ago -
 starlordsam26 reblogged this · 9 years ago
starlordsam26 reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 dreamshimmer liked this · 9 years ago
dreamshimmer liked this · 9 years ago -
 anwhite23 liked this · 9 years ago
anwhite23 liked this · 9 years ago -
 slytherin-grin-blog liked this · 9 years ago
slytherin-grin-blog liked this · 9 years ago -
 jheng1208-blog liked this · 9 years ago
jheng1208-blog liked this · 9 years ago -
 prsthrdt-blog reblogged this · 9 years ago
prsthrdt-blog reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 threehunnafrfr liked this · 9 years ago
threehunnafrfr liked this · 9 years ago -
 kuroinokokoro liked this · 9 years ago
kuroinokokoro liked this · 9 years ago -
 mikalrkayn liked this · 9 years ago
mikalrkayn liked this · 9 years ago -
 macluster769 liked this · 9 years ago
macluster769 liked this · 9 years ago -
 petunia-consciousness-blog liked this · 9 years ago
petunia-consciousness-blog liked this · 9 years ago -
 restless-muse-blog liked this · 9 years ago
restless-muse-blog liked this · 9 years ago -
 juniorsailmakermattcruse liked this · 9 years ago
juniorsailmakermattcruse liked this · 9 years ago -
 computer--cats reblogged this · 9 years ago
computer--cats reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 kiaraaileenirizarryrivera-blog liked this · 9 years ago
kiaraaileenirizarryrivera-blog liked this · 9 years ago -
 fleurdebach5-blog liked this · 9 years ago
fleurdebach5-blog liked this · 9 years ago -
 luxniccals liked this · 9 years ago
luxniccals liked this · 9 years ago -
 apologeticartist liked this · 9 years ago
apologeticartist liked this · 9 years ago -
 le0901-blog reblogged this · 9 years ago
le0901-blog reblogged this · 9 years ago -
 le0901-blog liked this · 9 years ago
le0901-blog liked this · 9 years ago
Explore the universe and discover our home planet with the official NASA Tumblr account
1K posts