Just Got A Week Of Clear Weather Will I Had Access To My Telescope, Managed To Get A Good Amount Of Data,
Just got a week of clear weather will I had access to my telescope, managed to get a good amount of data, treatment will have to wait though (I have some exams in 2 weeks). In the meantime, here's a quick test I did with the horse head nebula.

This is a SHH composition (there is nearly no OIII emission in this nebula and I did bother imaging in this wavelength).
More Posts from The-maddest-robot and Others

Photo of NGC 7000 / the North American nebula (southern part), the bright star on the top left corner is ξ Cygni. Might rework it later since this one still has a bit too much gradient/haze due to the full moon when I took the photos. In most cases, emission nebula are the result of gas clouds being ionised by the high energy UV radiation coming from very Hot (and often massive) stars/star cluster. In the case of NGC 7000 the star(s) responsible for most of the ionisation was an unknown for quite a long time, it is only in 2004 that the star responsible for the ionisation was located. This star (actually a binary system according to later publication) known as J205551.3+435225 is located behind the dark region of the nebula (bottom right corner of the photo) which explains why it was only recently identified.
(My best guess of the position of J205551.3+435225 in my picture according to what I can find in the original publication and in the SIMBAD database)


One last thing, that star was later nicknamed Bajamar Star, which comes from the original Spanish name for the Bahamas island.
For those not in the US wanting to search for dark skies near you, this website is quite useful.
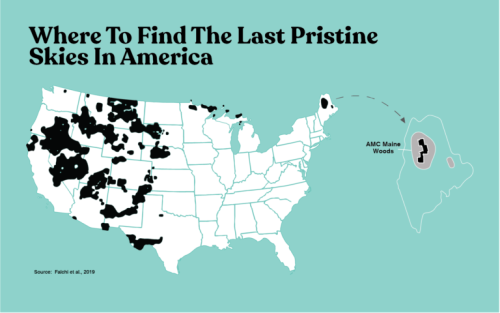
The black areas represent the remaining natural dark skies in the United States

This is the Crescent nebula it is located in the constellation Cygnus. This nebula is the result of the center star first becoming a red supergiant and ejecting some of its outer layers of gas in space, that gas cloud was then shaped into a bubble by the stellar winds emitted by the central star when it later turned into a Wolf–Rayet star.
The resulting gas bubble is heated and ionised by both the UV rays edited by the start and the stellar winds causing it to glow. Wolf-Rayet stars are the final step of some of the most massive stars before they explode into supernovas. In the case of the crescent nebula, the central star is expected to go supernova within the next few hundred thousand years (We probably still have quite a bit of time left before we observe that).

When a star goes supernova, some of the matter that composed the star is blasted off into space at extremely high velocities (up to 10% of the speed of light). This matter will then slowly (few hundred to a few tens of thousand of years) slow-down and cool-down to for me vast clouds of interstellar dust and gas. This second photo is a part of such a gas cloud, the veil nebula (the center of the western veil, also known as C34). In short, this is the photo of what's left of the corpse of a star that exploded about 10 to 20 thousand years ago.
Listen to the sound of wikipedia
This is a way to listen to changes to wikipedia. You are literally listening to knowledge being added to the world.
Pluck sounds are an addition, strings are subtractions, and the pitch says how how big the edit is. My heart shudders at this I love it so much.

Finale got around to processing the photos of M33 I had taken at the end of august. M33 is a spiral galaxy about half the size of our own galaxy and located about 2.7 million light years from earth. This galaxy has a rather high rate of star formation resulting in numerous ionised hydrogen regions (the red irregular blotches inside the galaxy), some of those being notable enough to have been included in the NGC catalogue or the IC catalogue.


NGC 588 NGC 604 (Example of some of the notable nebula in M33)
On of the first recorded observation of this galaxy was possibly done by Giovanni B. Hodierna before 1654, it was independently rediscovered by Charles Messier in 1764 who added it to his catalog (hence the name Messie 33).
information on the photo - total exposure time : 1h48 min using RGB and Ha filters - camera : ASI294 mm - telescope : Newtonian 150/600 with 0.95x coma corrector - photo edited with pixinsight
For those using PixInsight for treatment/edition, I recently discovered the scrips created by Seti Astro (https://www.setiastro.com/pjsr-scripts), Blemish-Blaster was quite useful to remove the halos from my Ha filter and What's In My Image helped with the identification of nebulas. If you had not heard those scrips, you should check them out.

Since the weather has been cloudy and rainy for about a month now (not a single night where I could take decent photos), here is a photo of the sun from last summer.
Despite the sun just looking like a bright ball of light at first glance, there are actually quite a lot of things to see on it.
This photo was taken using a specific light filter that enhances the details of the sun's surface. All of those black spots are sunspots, regions of the sun that are colder due to local magnetic fields preventing some of the heat from reaching the surface. The slightly brighter regions visible on the side of the sun are solar plage, zones that are slightly hotter, also due to the local magnetic fields.
Finally, the surface of the sun in the picture looks a bit granular/wrought, that is due to solar granulation, smaller (around 1000 km in width) convection currents (basically bubble of plasma) at the surface. (The resolution isn't great so the granulation is not super clearly visible, unfortunately).

Ok, so I was searching for information on some of the objects visible in my photo of the horse head nebula and I found these two posts (Reddit and Astrobin) by DanielZoliro that also used a SII and Ha combination but with a slightly different processing (Notably, the RGB combination being R: SII, G: 0.6xHa + 0.4xSII, B: Ha). I loved his results and I had to try it with my own data. Did turn out great, but there was a reflection of a star on the SII data and this processing amplified it (the big reddish round/donut thing on right of the full image).

(Image taken using a CarbonStar 150/600 newtonian telescope with a 0.95 coma corrector, ZWO ASI294 monochrome camera and Baader 6.5nm SHO filter. 5x120s image for each colour filter (RGB), 22x300s for the Ha filter and 32x300s for the SII filter, total imaging time 5h, stacking and processing done in PixInsight.)
This reminded me of the isonitrile freezer at my previous internship.
For those who don't know, isonitriles (aka isocyanides) are a class of compounds that contain this motif:

They are known to smell very bad and many synthesis pathways to those compounds were discovered because of their stench. (I personally think they smell like a mixture of rotten cabbage and burned rubber but more ''artificial'')
So in that lab, we had a freezer dedicated to them, and even with sealed bottles in à -20°C freezers in a separated and ventilated cabinet, you would still be able to detect their odour if you stood next to it (not strongly, but still detectable).
We had to move that freezer to a new lab, it stayed unplugged for 15 to 20 minutes, and in the 5 minutes we need to power it back in the new lab, the entire room had filled with that isonitrile stench (mind you that freezer had not been open during the entire operation). Thankfully we did that on a Friday afternoon and by Monday the smell had disappeared.
Just for reference this is from the MSDS of benzyl isonitrile :


found on a fridge in my lab, haha

Photo of the Pleiades (Messier 45) I took to test my new telescope. This is an open cluster of stars situated about 440 light years from earth, the brighter stars of the cluster are visible with the naked eye (around 5 to 10 stars visible depending of the light pollution, weather and eye accommodation do darkness). Unfortunately, the nebulosity, which I composed of dust clouds reflecting the light from the bright stars, is only visible in photos or with (relatively) large telescope. The cluster is about 100 million years old which is young (for an astronomical object), the more visible stars are hot blue giants, but many other, less visible, stars are present in the cluster. This cluster due to its high visibility has taken an important place in many cultures and mythologies.
(as a fun fact the name of M45 in Japanese is Subaru, and yes the car brand dose gets its name for this star cluster (which explains the logo of the brand))



Those do not look like much, but they are, to the best of my knowledge, Herbig-Haro object (to left: HH 94, top right: HH 249 and bottom: HH 95) Herbig-Haro object are ionised gas clouds formed when the jet of hot plasma ejected at the poles of newly born stars interacts with Interstellar gas, they are thus more common in star forming regions. I first noticed one of them (HH 94) after I shared the image with a friend. The What's in my image PixInsight scrip from SetiAstro was very useful in finding out what that was. I couldn't find a lot of information on those objects specifically (and very few pictures), but a few publications did have images to compare with (orientation differs):


(original publication ref for HH 94 & HH 95; additional publication ref for HH294 aka NGC 2023 HH 3) (better images of other Herbig-Haro object taken by Hubble : 1, 2 & 3) Position of the three objects in the original image (another might be present but I wasn't confident they were visible):

-
 trash-shay liked this · 3 months ago
trash-shay liked this · 3 months ago -
 angrygonk liked this · 3 months ago
angrygonk liked this · 3 months ago -
 cosmetreee reblogged this · 4 months ago
cosmetreee reblogged this · 4 months ago -
 cosmetreee liked this · 4 months ago
cosmetreee liked this · 4 months ago -
 roxygobyebye liked this · 4 months ago
roxygobyebye liked this · 4 months ago -
 kb1301 liked this · 4 months ago
kb1301 liked this · 4 months ago -
 ginsso reblogged this · 4 months ago
ginsso reblogged this · 4 months ago -
 gil-notskajla liked this · 4 months ago
gil-notskajla liked this · 4 months ago -
 freelightpandahumanoid liked this · 4 months ago
freelightpandahumanoid liked this · 4 months ago -
 cryoquicksilver liked this · 4 months ago
cryoquicksilver liked this · 4 months ago -
 murphybyzantine liked this · 4 months ago
murphybyzantine liked this · 4 months ago -
 esamadnan reblogged this · 4 months ago
esamadnan reblogged this · 4 months ago -
 youwerebornbluerthanabutterfly liked this · 4 months ago
youwerebornbluerthanabutterfly liked this · 4 months ago -
 tiredbadger liked this · 4 months ago
tiredbadger liked this · 4 months ago -
 johntheforrunner liked this · 4 months ago
johntheforrunner liked this · 4 months ago -
 sin-city-sights liked this · 4 months ago
sin-city-sights liked this · 4 months ago -
 silvereyedowl reblogged this · 4 months ago
silvereyedowl reblogged this · 4 months ago -
 silvereyedowl liked this · 4 months ago
silvereyedowl liked this · 4 months ago -
 shaythempronouns liked this · 4 months ago
shaythempronouns liked this · 4 months ago -
 the-maddest-robot reblogged this · 4 months ago
the-maddest-robot reblogged this · 4 months ago

Astrophotographer & chemist, mid 20'sCurrently on the roof yelling at the clouds to get out of the wayMostly astrophotos I've taken, possibly other science related stuff
51 posts