20.1.18 // Studygram: Alimastudies

20.1.18 // studygram: alimastudies
i don’t normally upload pictures of my homework because i don’t tend to spend a lot of effort or time on them as i know i won’t be using it again, but for this biology homework i thought i would do it nicely and use it for my future notes! i need to work on my handlettering oh dear god ahhh i used a crayola supertip for it
More Posts from T-b-a-blr-blog and Others
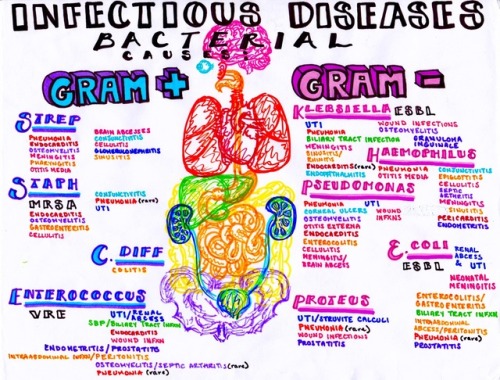
Infectious bacterial diseases and where to find them


18/1/18 - Recent virology notes! Ignore the headings, I bought some new brush pens and I’m still getting used to them..

INSTAGRAM | ETSY | PINTEREST | BLOG

Petechial hemorrhages on palms of hand in Rocky mountain spotted fever due to Rickettsia rickettsii: In RMSF, the petechial rash begins on the palms and spreads to the trunk.

Endospore

it’s technically kinda busy work but i still love it


Medically Important Fungi

13.02.18 Revision
I’ve always got my trusty reference book with me at work, but sometimes I like to read over a few topics just in case anything ever shows up :) and oml trying to write referral letter templates be like: …has been measuring … measured between 5-12 mmol/L … BGL measuring between 5-12 mmol/L OTL
🎼 The Boots - Gugudan 구구단
Follow optomstudies for daily original posts and study masterposts! Links: all originals + langblr posts + 15-part college 101 series + web directory!

Diphtheria is known for creating a slimy/sticky/smelly exudate in the throat and mouth, but there are quite a few variations on its etiology and presentation.
A. Common type of diphtheria. Child three years old, seen on fourth day of illness. Exudate covering pharynx, tonsils, and uvula. Received 16,000 units of antitoxin. Throat clear on sixth day. Discharged cured.
B. Follicular type of diphtheria. Child seven years old, seen on second day of illness. The membrane involved the lacunae of the tonsils. Resembles follicular tonsillitis. Received 6,000 units of antitoxin total.
C. Hemorrhagic type of diphtheria. Child seven-and-a-half years old, seen on sixth day of illness. Tonsillar and post-pharyngeal exudate. Severe nasal and post-pharyngeal hemorrhages during exfoliation of membrane. Received in all 15,000 units of antitoxin. Throat clear on ninth day of illness. Myocarditis developed. Case discharged cured four weeks after admission.
D. Septic type of diphtheria. Child eight years old, seen on fifth day of illness. The pseudo-membrane in this case covered the hard palate and extended in one large mass down the pharynx, completely hiding the tonsils.
Diseases of Infancy and Childhood. Louis Fischer, M.D., 1917.
Neisseria gonorrhoeae


PMN filled with Neisseria gonorrhoeae => Gram- diplococci, glucose fermenter, non maltose fermenter, oxidase positive.
Very inflammatory response: exudate with high number of PMN. TX with ceftriaxone and always ALWAYS test for Chlamydia trachomatis (since is more common and exudate is similar)
How to tell them apart?
N. gonorrhoeae’s exudate is more purulent than C. trachomatis.
N. gonorrhoeae’s exudate is “greenish-yellowish” but C. trachomatis’s is whiter.
N. gonorrhoeae is always inside a PMN while C. trachomatis is not

Grows in Thayer-Martin medium (chocolote agar + antibiotics, is a selective medium)
-
 calmnessisasuperpower liked this · 5 months ago
calmnessisasuperpower liked this · 5 months ago -
 fatimagpx liked this · 3 years ago
fatimagpx liked this · 3 years ago -
 futuredoctorquick reblogged this · 4 years ago
futuredoctorquick reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 studigoals liked this · 4 years ago
studigoals liked this · 4 years ago -
 dr-vanillabear liked this · 4 years ago
dr-vanillabear liked this · 4 years ago -
 witchylillie liked this · 4 years ago
witchylillie liked this · 4 years ago -
 st-udying reblogged this · 5 years ago
st-udying reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 millyyandrews liked this · 5 years ago
millyyandrews liked this · 5 years ago -
 sweatyhoundknighthairdo-blog liked this · 5 years ago
sweatyhoundknighthairdo-blog liked this · 5 years ago -
 jsmarcelo-blog liked this · 5 years ago
jsmarcelo-blog liked this · 5 years ago -
 creatingabrooke liked this · 5 years ago
creatingabrooke liked this · 5 years ago -
 raven-nole liked this · 5 years ago
raven-nole liked this · 5 years ago -
 inamoroto liked this · 5 years ago
inamoroto liked this · 5 years ago -
 jellyfishmovingout reblogged this · 5 years ago
jellyfishmovingout reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 anastomosis liked this · 5 years ago
anastomosis liked this · 5 years ago -
 sharonsharonsharonsharonsharon liked this · 5 years ago
sharonsharonsharonsharonsharon liked this · 5 years ago -
 peacatchyou liked this · 5 years ago
peacatchyou liked this · 5 years ago -
 kyuusblog liked this · 5 years ago
kyuusblog liked this · 5 years ago -
 stupendousclodhumangiant-blog liked this · 5 years ago
stupendousclodhumangiant-blog liked this · 5 years ago -
 janisha27 reblogged this · 5 years ago
janisha27 reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 velarostudies reblogged this · 5 years ago
velarostudies reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 tampongrease liked this · 5 years ago
tampongrease liked this · 5 years ago -
 kpopstudying liked this · 6 years ago
kpopstudying liked this · 6 years ago -
 pinkreho liked this · 6 years ago
pinkreho liked this · 6 years ago -
 honeysweetthalia liked this · 6 years ago
honeysweetthalia liked this · 6 years ago -
 thewayforward reblogged this · 6 years ago
thewayforward reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 marcelineminxxx liked this · 6 years ago
marcelineminxxx liked this · 6 years ago -
 overeducated reblogged this · 6 years ago
overeducated reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 hinoko1 liked this · 6 years ago
hinoko1 liked this · 6 years ago -
 diananiburski liked this · 6 years ago
diananiburski liked this · 6 years ago -
 main10ants liked this · 6 years ago
main10ants liked this · 6 years ago -
 rememberthelaughs reblogged this · 6 years ago
rememberthelaughs reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 kristijenner19 liked this · 6 years ago
kristijenner19 liked this · 6 years ago -
 study-habit reblogged this · 6 years ago
study-habit reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 dopepaperdiplomatplaid-blog liked this · 6 years ago
dopepaperdiplomatplaid-blog liked this · 6 years ago -
 rubyetadams liked this · 6 years ago
rubyetadams liked this · 6 years ago -
 littleeginger liked this · 6 years ago
littleeginger liked this · 6 years ago -
 studycentrc reblogged this · 6 years ago
studycentrc reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 studyland-blog reblogged this · 6 years ago
studyland-blog reblogged this · 6 years ago