Celebrating 81 Years Of Ingenuity
Celebrating 81 Years of Ingenuity

Eighty-one years ago, our world-class research center in California’s Silicon Valley was born. Ground broke on Ames Research Center on Dec. 20, 1939. It was the second aeronautical laboratory established by the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics to perform fundamental research on all things flight. From its very beginnings, Ames was a place for innovation. Tests performed in its wind tunnels transformed military aircraft during World War II and paved the way for air travel at supersonic speeds. In the 1950s and ‘60s, its researchers looked to the stars and came up with new designs and materials for spacecraft that would make human spaceflight a reality. Fast-forward to the present, and the center contributes to virtually every major agency mission through its expertise in spacecraft entry systems, robotics, aeronautics, supercomputing, and so much more! Here are things to know about Ames.
Ames Research Center is home to the world’s largest wind tunnel.

The center is also home to Pleiades, our most powerful supercomputer.

Its modeling and simulation work plays a key role in designing new vehicles for exploring space.

The center invented heat shield materials for landing rovers on Mars.

It built robots to assist astronauts living and working aboard the International Space Station.

It launched a space telescope that revealed thousands of worlds beyond our solar system.

The center has also led multiple missions to explore the Moon.

It found water on the Moon ... more than once, and in places no one would have guessed.

The Volatiles Investigating Polar Exploration Rover is the latest lunar exploration mission led by Ames. Launching in 2023, the mobile robot will search for water ice inside craters and other places at the Moon's South Pole. Its survey will help pave the way for astronaut missions to the lunar surface beginning in 2024 as part of the Artemis program.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
More Posts from Nasa and Others
Solar System: Things to Know This Week
Reaching out into space yields benefits on Earth. Many of these have practical applications — but there's something more than that. Call it inspiration, perhaps, what photographer Ansel Adams referred to as nature's "endless prospect of magic and wonder."
Our ongoing exploration of the solar system has yielded more than a few magical images. Why not keep some of them close by to inspire your own explorations? This week, we offer 10 planetary photos suitable for wallpapers on your desktop or phone. Find many more in our galleries. These images were the result of audacious expeditions into deep space; as author Edward Abbey said, "May your trails be crooked, winding, lonesome, dangerous, leading to the most amazing view."

1. Martian Selfie
This self-portrait of NASA's Curiosity Mars rover shows the robotic geologist in the "Murray Buttes" area on lower Mount Sharp. Key features on the skyline of this panorama are the dark mesa called "M12" to the left of the rover's mast and pale, upper Mount Sharp to the right of the mast. The top of M12 stands about 23 feet (7 meters) above the base of the sloping piles of rocks just behind Curiosity. The scene combines approximately 60 images taken by the Mars Hand Lens Imager, or MAHLI, camera at the end of the rover's robotic arm. Most of the component images were taken on September 17, 2016.
800 x 600
1024 x 768
1280 x 1024
1600 x 1200
1280 x 800
1440 x 900
1920 x 1200

2. The Colors of Pluto
NASA's New Horizons spacecraft captured this high-resolution, enhanced color view of Pluto on July 14, 2015. The image combines blue, red and infrared images taken by the Ralph/Multispectral Visual Imaging Camera (MVIC). Pluto's surface sports a remarkable range of subtle colors, enhanced in this view to a rainbow of pale blues, yellows, oranges, and deep reds. Many landforms have their own distinct colors, telling a complex geological and climatological story that scientists have only just begun to decode.
800 x 600
1024 x 768
1280 x 1024
1600 x 1200
1280 x 800
1440 x 900
1920 x 1200

3. The Day the Earth Smiled
On July 19, 2013, in an event celebrated the world over, our Cassini spacecraft slipped into Saturn's shadow and turned to image the planet, seven of its moons, its inner rings — and, in the background, our home planet, Earth. This mosaic is special as it marks the third time our home planet was imaged from the outer solar system; the second time it was imaged by Cassini from Saturn's orbit, the first time ever that inhabitants of Earth were made aware in advance that their photo would be taken from such a great distance.
800 x 600
1024 x 768
1280 x 1024
1600 x 1200
1280 x 800
1440 x 900
1920 x 1200

4. Looking Back
Before leaving the Pluto system forever, New Horizons turned back to see Pluto backlit by the sun. The small world's haze layer shows its blue color in this picture. The high-altitude haze is thought to be similar in nature to that seen at Saturn's moon Titan. The source of both hazes likely involves sunlight-initiated chemical reactions of nitrogen and methane, leading to relatively small, soot-like particles called tholins. This image was generated by combining information from blue, red and near-infrared images to closely replicate the color a human eye would perceive.
800 x 600
1024 x 768
1280 x 1024
1600 x 1200
1280 x 800
1440 x 900
1920 x 1200

5. Catching Its Own Tail
A huge storm churning through the atmosphere in Saturn's northern hemisphere overtakes itself as it encircles the planet in this true-color view from Cassini. This picture, captured on February 25, 2011, was taken about 12 weeks after the storm began, and the clouds by this time had formed a tail that wrapped around the planet. The storm is a prodigious source of radio noise, which comes from lightning deep within the planet's atmosphere.
800 x 600
1024 x 768
1280 x 1024
1600 x 1200
1280 x 800
1440 x 900
1920 x 1200

6. The Great Red Spot
Another massive storm, this time on Jupiter, as seen in this dramatic close-up by Voyager 1 in 1979. The Great Red Spot is much larger than the entire Earth.
800 x 600
1024 x 768
1280 x 1024
1600 x 1200
1280 x 800
1440 x 900
1920 x 1200

7. More Stormy Weather
Jupiter is still just as stormy today, as seen in this recent view from NASA's Juno spacecraft, when it soared directly over Jupiter's south pole on February 2, 2017, from an altitude of about 62,800 miles (101,000 kilometers) above the cloud tops. From this unique vantage point we see the terminator (where day meets night) cutting across the Jovian south polar region's restless, marbled atmosphere with the south pole itself approximately in the center of that border. This image was processed by citizen scientist John Landino. This enhanced color version highlights the bright high clouds and numerous meandering oval storms.
800 x 600
1024 x 768
1280 x 1024
1600 x 1200
1280 x 800
1440 x 900
1920 x 1200

8. X-Ray Vision
X-rays stream off the sun in this image showing observations from by our Nuclear Spectroscopic Telescope Array, or NuSTAR, overlaid on a picture taken by our Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO). The NuSTAR data, seen in green and blue, reveal solar high-energy emission. The high-energy X-rays come from gas heated to above 3 million degrees. The red channel represents ultraviolet light captured by SDO, and shows the presence of lower-temperature material in the solar atmosphere at 1 million degrees.
800 x 600
1024 x 768
1280 x 1024
1600 x 1200
1280 x 800
1440 x 900
1920 x 1200

9. One Space Robot Photographs Another
This image from NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter shows Victoria crater, near the equator of Mars. The crater is approximately half a mile (800 meters) in diameter. It has a distinctive scalloped shape to its rim, caused by erosion and downhill movement of crater wall material. Since January 2004, the Mars Exploration Rover Opportunity has been operating in the region where Victoria crater is found. Five days before this image was taken in October 2006, Opportunity arrived at the rim of the crater after a drive of more than over 5 miles (9 kilometers). The rover can be seen in this image, as a dot at roughly the "ten o'clock" position along the rim of the crater. (You can zoom in on the full-resolution version here.)
800 x 600
1024 x 768
1280 x 1024
1600 x 1200
1280 x 800
1440 x 900
1920 x 1200

10. Night Lights
Last, but far from least, is this remarkable new view of our home planet. Last week, we released new global maps of Earth at night, providing the clearest yet composite view of the patterns of human settlement across our planet. This composite image, one of three new full-hemisphere views, provides a view of the Americas at night from the NASA-NOAA Suomi-NPP satellite. The clouds and sun glint — added here for aesthetic effect — are derived from MODIS instrument land surface and cloud cover products.
Full Earth at night map
Americas at night
Discover more lists of 10 things to know about our solar system HERE.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Solar System: Things to Know This Week
Follow our Juno craft during a close flyby of Jupiter, learn about Cassini’s final mission during a Facebook live event (in case you missed it) and more!

1. Jupiter, Up Close
Our Juno mission completed a close flyby of Jupiter on Thursday, February 2, its latest science orbit of the mission. All of Juno's science instruments and the spacecraft's JunoCam were operating during the flyby to collect data that is now being returned to Earth.

Want to know more? Using NASA's Eyes on the Solar System and simulated data from the Juno flight team you can ride onboard the Juno spacecraft in real-time at any moment during the entire mission.

2. In Case You Missed It--Cassini Facebook Live
Cassini Project Scientist Linda Spilker and mission planner Molly Bittner take questions about the mission's "Ring-Grazing" orbits during Facebook Live. Watch it now: www.facebook.com/NASA/videos/10154861046561772/

3. Cassini Scientist for a Day Essay Contest
The deadline is Friday, February 24 for U.S. student in grades 5 to 12. For international students, visit the page for more info!
More: solarsystem.nasa.gov/educ/Scientist-For-a-Day/2016-17/videos/intro

4. Cassini Spies Dione
Dione's lit hemisphere faces away from Cassini's camera, yet the moon's darkened surface are dimly illuminated in this image, due to the phenomenon of Saturnshine. Although direct sunlight provides the best illumination for imaging, light reflected off of Saturn can do the job as well. In this image, Dione (698 miles or 1,123 kilometers across) is above Saturn's day side, and the moon's night side is faintly illuminated by sunlight reflected off the planet's disk.
Discover the full list of 10 things to know about our solar system this week HERE.
Follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Solar System: Things to Know This Week

For the first time in almost a decade, we're going back to Jupiter. Our Juno spacecraft arrives at the king of planets on the fourth of July. From a unique polar orbit, Juno will repeatedly dive between the planet and its intense belts of charged particle radiation. Juno's primary goal is to improve our understanding of Jupiter's formation and evolution, which will help us understand the history of our own solar system and provide new insight into how other planetary systems form.
In anticipation, here are a few things you need to know about the Juno mission and the mysterious world it will explore:
1. This is the Big One

The most massive planet in our solar system, with dozens of moons and an enormous magnetic field, Jupiter rules over a kind of miniature solar system.
2. Origin Story

Why study Jupiter in the first place? How does the planet fit into the solar system as a whole? What is it hiding? How will Juno unlock its secrets? A series of brief videos tells the stories of Jupiter and Juno. Watch them HERE.
3. Eyes on Juno
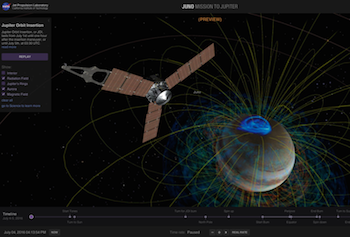
If you really want a hands-on understanding of Juno's flight through the Jupiter system, there's no better tool than the "Eyes on Juno" online simulation. It uses data from the mission to let you realistically see and interact with the spacecraft and its trajectory—in 3D and across both time and space.
4. You’re on JunoCam!

Did you know that you don't have to work for NASA to contribute to the Juno mission? Amateur astronomers and space enthusiasts everywhere are invited to help with JunoCam, the mission's color camera. You can upload your own images of Jupiter, comment on others' images, and vote on which pictures JunoCam will take when it reaches the Jovian system.
5. Ride Along
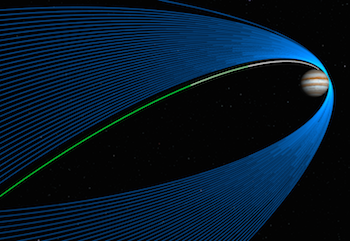
It's easy to follow events from the Juno mission as they unfold. Here are several ways to follow along online:
Want to learn more? Read our full list of the 10 things to know this week about the solar system HERE.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Space Gardening 101
You can’t escape eating (or gardening!) your vegetables, even if you’re in space. On Aug. 10, astronauts on the International Space Station sampled their first space grown salad. This freshly harvest red romaine lettuce was grown in the “Veggie” plant growth chamber that is designed to make gardens flourish in weightlessness.

In a weightless environment, there is no up and down, so roots grow in all directions. Water and soil, the materials used to anchor these plants and allow for root growth tend to float away.
How Do We Grow Plants in Space?
1. Plant Pillows

The Veggie chamber helps solve the problems of a weightless environment by using ‘plant pillows’, sounds comfy right? These pillows are bags filled with material for growing plants in space.
2. Wicks

Wicks are implanted into the bags and are used to draw water from inside the pillow to the plant.

These wicks also provide a place to glue the seeds. It’s important to orient the seeds so roots will grow ‘down’, and shoots that emerge will push out of the bag.
3. LED Lights

LED lights are used for photosynthesis and give the shoots a sense of direction so they keep growing upward. The walls of the Veggie chamber can expand to make room for the plant as it grows.
The purple/pinkish hue surrounding the plants in Veggie is the result of a combination of the red and blue lights, which is what the plants need to grow. Green LEDS were added so the plants look like edible food rather than weird purple plants.
Why are we growing plants in space?
When astronauts travel on deep space missions, like Mars, they will need to be self-sufficient for long periods of time. Having the ability to grow their own food is a big step in that direction. There is also a desire to grow flowering vegetables in space, which is why we are currently tending to zinnia flowers on orbit. Growing these flowering plants will help us understand longer duration growing plants that have to flower in space, such as tomatoes.

What’s Next? The next SpaceX delivery will include seeds for a small cabbage and additional red romaine lettuce. Upcoming experiments will use various ratios of red and blue lights and different fertilizers in attempts to improve crop yield, nutrition and flavor. The findings from these experiments can be utilized both on Earth and in space.

In addition to the nutrition benefits of growing vegetables in space, the psychological benefits are also significant. Having living plants can help with stress and increase the crews’ enjoyment. It provides the sights, smells and tastes of Earth.
To learn more about gardening in space, watch ScienceCast HERE.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
We Need Your Help to Find STEVE
Glowing in mostly purple and green colors, a newly discovered celestial phenomenon is sparking the interest of scientists, photographers and astronauts. The display was initially discovered by a group of citizen scientists who took pictures of the unusual lights and playfully named them "Steve."
When scientists got involved and learned more about these purples and greens, they wanted to keep the name as an homage to its initial name and citizen science discoverers. Now it is STEVE, short for Strong Thermal Emission Velocity Enhancement.

Credit: ©Megan Hoffman
STEVE occurs closer to the equator than where most aurora appear – for example, Southern Canada – in areas known as the sub-auroral zone. Because auroral activity in this zone is not well researched, studying STEVE will help scientists learn about the chemical and physical processes going on there. This helps us paint a better picture of how Earth's magnetic fields function and interact with charged particles in space. Ultimately, scientists can use this information to better understand the space weather near Earth, which can interfere with satellites and communications signals.

Want to become a citizen scientist and help us learn more about STEVE? You can submit your photos to a citizen science project called Aurorasaurus, funded by NASA and the National Science Foundation. Aurorasaurus tracks appearances of auroras – and now STEVE – around the world through reports and photographs submitted via a mobile app and on aurorasaurus.org.
Here are six tips from what we have learned so far to help you spot STEVE:
1. STEVE is a very narrow arc, aligned East-West, and extends for hundreds or thousands of miles.

Credit: ©Megan Hoffman
2. STEVE mostly emits light in purple hues. Sometimes the phenomenon is accompanied by a short-lived, rapidly evolving green picket fence structure (example below).

Credit: ©Megan Hoffman
3. STEVE can last 20 minutes to an hour.
4. STEVE appears closer to the equator than where normal – often green – auroras appear. It appears approximately 5-10° further south in the Northern hemisphere. This means it could appear overhead at latitudes similar to Calgary, Canada. The phenomenon has been reported from the United Kingdom, Canada, Alaska, northern US states, and New Zealand.

5. STEVE has only been spotted so far in the presence of an aurora (but auroras often occur without STEVE). Scientists are investigating to learn more about how the two phenomena are connected.
6. STEVE may only appear in certain seasons. It was not observed from October 2016 to February 2017. It also was not seen from October 2017 to February 2018.

Credit: ©Megan Hoffman
STEVE (and aurora) sightings can be reported at www.aurorasaurus.org or with the Aurorasaurus free mobile apps on Android and iOS. Anyone can sign up, receive alerts, and submit reports for free.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
What are the moments when you think to yourself "yes. THIS is why I love my job"..? ✨
What is some advice that really helped you get to where you are now?

In case you missed it earlier in July, here’s a look at how our view of Pluto has changed over the course of several decades. The first frame is a digital zoom-in on Pluto as it appeared upon its discovery by Clyde Tombaugh in 1930 (image courtesy Lowell Observatory Archives). The other images show various views of Pluto as seen by NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope beginning in the 1990s and NASA’s New Horizons spacecraft in 2015. The final sequence zooms in to a close-up frame of Pluto released on July 15, 2015.
This amazing view of details on Pluto came via New Horizons, which launched on Jan. 19, 2006. New Horizons swung past Jupiter for a gravity boost and scientific studies in February 2007, and conducted a reconnaissance flyby study of Pluto and its moons in summer 2015. Pluto closest approach occurred on July 14, 2015. As part of an extended mission, the spacecraft is expected to head farther into the Kuiper Belt to examine one or two of the ancient, icy mini-worlds in that vast region, at least a billion miles beyond Neptune’s orbit.
Image credits available here.
13 Reasons to Have an Out-of-This-World Friday (the 13th)
1. Not all of humanity is bound to the ground

Since 2000, the International Space Station has been continuously occupied by humans. There, crew members live and work while conducting important research that benefits life on Earth and will even help us eventually travel to deep space destinations, like Mars.
2. We’re working to develop quieter supersonic aircraft that would allow you to travel from New York to Los Angeles in 2 hours

We are working hard to make flight greener, safer and quieter – all while developing aircraft that travel faster, and building an aviation system that operates more efficiently. Seventy years after Chuck Yeager broke the sound barrier in the Bell X-1 aircraft, we’re continuing that supersonic X-plane legacy by working to create a quieter supersonic jet with an aim toward passenger flight.
3. The spacecraft, rockets and systems developed to send astronauts to low-Earth orbit as part of our Commercial Crew Program is also helping us get to Mars
Changes to the human body during long-duration spaceflight are significant challenges to solve ahead of a mission to Mars and back. The space station allows us to perform long duration missions without leaving Earth’s orbit.

Although they are orbiting Earth, space station astronauts spend months at a time in near-zero gravity, which allows scientists to study several physiological changes and test potential solutions. The more time they spend in space, the more helpful the station crew members can be to those on Earth assembling the plans to go to Mars.
4. We’re launching a spacecraft in 2018 that will go “touch the Sun”

In the summer of 2018, we’re launching Parker Solar Probe, a spacecraft that will get closer to the Sun than any other in human history. Parker Solar Probe will fly directly through the Sun’s atmosphere, called the corona. Getting better measurements of this region is key to understanding our Sun.
For instance, the Sun releases a constant outflow of solar material, called the solar wind. We think the corona is where this solar wind is accelerated out into the solar system, and Parker Solar Probe’s measurements should help us pinpoint how that happens.
5. You can digitally fly along with spacecraft…that are actually in space…in real-time!

NASA’s Eyes are immersive, 3D simulations of real events, spacecraft locations and trajectories. Through this interactive app, you can experience Earth and our solar system, the universe and the spacecraft exploring them. Want to watch as our Juno spacecraft makes its next orbit around Juno? You can! Or relive all of the Voyager mission highlights in real-time? You can do that too! Download the free app HERE to start exploring.
6. When you feel far away from home, you can think of the New Horizons spacecraft as it heads toward the Kuiper Belt, and the Voyager spacecraft are beyond the influence of our sun…billions of miles away

Our New Horizons spacecraft completed its Pluto flyby in July 2015 and has continued on its way toward the Kuiper Belt. The spacecraft continues to send back important data as it travels toward deeper space at more than 32,000 miles per hour, and is ~3.2 billion miles from Earth.

In addition to New Horizons, our twin Voyager 1 and 2 spacecraft are exploring where nothing from Earth has flown before. Continuing on their more-than-37-year journey since their 1977 launches, they are each much farther away from Earth and the sun than Pluto. In August 2012, Voyager 1 made the historic entry into interstellar space, the region between the stars, filled with material ejected by the death of nearby stars millions of years ago.
7. There are humans brave enough to not only travel in space, but venture outside space station to perform important repairs and updates during spacewalks

Just this month (October 2017) we’ve already had two spacewalks on the International Space Station...with another scheduled on Oct. 20.
Spacewalks are important events where crew members repair, maintain and upgrade parts of the International Space Station. These activities can also be referred to as EVAs – Extravehicular Activities. Not only do spacewalks require an enormous amount of work to prepare for, but they are physically demanding on the astronauts. They are working in the vacuum of space in only their spacewalking suit.
8. Smart people are up all night working in control rooms all over NASA to ensure that data keeps flowing from our satellites and spacecraft

Our satellites and spacecraft help scientists study Earth and space. Missions looking toward Earth provide information about clouds, oceans, land and ice. They also measure gases in the atmosphere, such as ozone and carbon dioxide and the amount of energy that Earth absorbs and emits. And satellites monitor wildfires, volcanoes and their smoke.
9. A lot of NASA-developed tech has been transferred for use to the public
Our Technology Transfer Program highlights technologies that were originally designed for our mission needs, but have since been introduced to the public market. HERE are a few spinoff technologies that you might not know about.
10. We have a spacecraft currently traveling to an asteroid to collect a sample and bring it back to Earth

OSIRIS-REx is our first-ever mission that will travel to an asteroid and bring a sample of it back to Earth. Currently, the spacecraft is on its way to asteroid Bennu where it will survey and map the object before it “high-fives” the asteroid with its robotic arm to collect a sample, which it will send to Earth.
If everything goes according to plan, on Sept. 24, 2023, the capsule containing the asteroid sample will make a soft landing in the Utah desert.
11. There are Earth-sized planets outside our solar system that may be habitable
To date, we have confirmed 3,000+ exoplanets, which are planets outside our solar system that orbit a Sun-like star. Of these 3,000, some are in the habitable zone – where the temperature is just right for liquid water to exist on the surface.

Recently, our Spitzer Space Telescope revealed the first known system of SEVEN Earth-size planets around a single star. Three of these plants are firmly in the habitable zone, and could have liquid water on the surface, which is key to life as we know it.
12. Earth looks like art from space

In 1960, the United States put its first Earth-observing environmental satellite into orbit around the planet. Over the decades, these satellites have provided invaluable information, and the vantage point of space has provided new perspectives on Earth.

The beauty of Earth is clear, and the artistry ranges from the surreal to the sublime.
13. We’re building a telescope that will be able to see the first stars ever formed in the universe

Wouldn’t it be neat to see a period of the universe’s history that we’ve never seen before? That’s exactly what the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) will be able to do…plus more!
Specifically, Webb will see the first objects that formed as the universe cooled down after the Big Bang. We don’t know exactly when the universe made the first stars and galaxies – or how for that matter. That is what we are building Webb to help answer.
Happy Friday the 13th! We hope it’s out-of-this-world!
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
Hot & Steamy RS-25 Engine Test

Today, we tested the RS-25 engine at Stennis Space Center in Mississippi, and boy was it hot! Besides the fact that it was a hot day, the 6,000 degree operating temperature of the hot fire test didn’t help things. This engine is one of four that will power the core stage of our Space Launch System (SLS) into deep space and to Mars. Today’s test reached 109% power and burned 150,000 gallons of liquid oxygen and 60,000 gallons of liquid hydrogen. When SLS launches with all 4 of its engines, it will be the most powerful rocket in the world!

This engine was previously used to to fly dozens of successful missions on the space shuttle, so you might be asking, “Why are we spending time testing it again if we already know it’s awesome?” Well, it’s actually really important that we test them specifically for use with SLS for a number of reasons, including the fact that we will be operating at 109% power, vs. the 104% power previously used.

If you missed the 535-second, ground rumbling test today -- you’re in luck. We’ve compiled all the cool stuff (fire, steam & loud noises) into a recap video. Check it out here:
-
 tristapena777 liked this · 2 years ago
tristapena777 liked this · 2 years ago -
 victorreid liked this · 3 years ago
victorreid liked this · 3 years ago -
 skarletchronicles liked this · 3 years ago
skarletchronicles liked this · 3 years ago -
 canigohomenow02 liked this · 4 years ago
canigohomenow02 liked this · 4 years ago -
 mawusifitnesstraining liked this · 4 years ago
mawusifitnesstraining liked this · 4 years ago -
 edsonlima17 liked this · 4 years ago
edsonlima17 liked this · 4 years ago -
 melissathecat liked this · 4 years ago
melissathecat liked this · 4 years ago -
 usafphantom2 reblogged this · 4 years ago
usafphantom2 reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 usafphantom2 liked this · 4 years ago
usafphantom2 liked this · 4 years ago -
 focusas reblogged this · 4 years ago
focusas reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 preserve-or-raze liked this · 4 years ago
preserve-or-raze liked this · 4 years ago -
 fantasticcollectortragedysb-blog liked this · 4 years ago
fantasticcollectortragedysb-blog liked this · 4 years ago -
 sherlocksittinginthelittlecouch liked this · 4 years ago
sherlocksittinginthelittlecouch liked this · 4 years ago -
 danielnaturelover liked this · 4 years ago
danielnaturelover liked this · 4 years ago -
 breathtakingwonders liked this · 4 years ago
breathtakingwonders liked this · 4 years ago -
 deglorath liked this · 4 years ago
deglorath liked this · 4 years ago -
 sibeliusborges-blog liked this · 4 years ago
sibeliusborges-blog liked this · 4 years ago -
 youare65 liked this · 4 years ago
youare65 liked this · 4 years ago -
 the-cerulean-seal reblogged this · 4 years ago
the-cerulean-seal reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 soohfanni liked this · 4 years ago
soohfanni liked this · 4 years ago -
 ateezofficialsblog liked this · 4 years ago
ateezofficialsblog liked this · 4 years ago -
 hano-orion liked this · 4 years ago
hano-orion liked this · 4 years ago -
 blogjorgefotos reblogged this · 4 years ago
blogjorgefotos reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 blogjorgefotos liked this · 4 years ago
blogjorgefotos liked this · 4 years ago -
 gtunesmiff liked this · 4 years ago
gtunesmiff liked this · 4 years ago -
 butyoutoldmeiwasfunny reblogged this · 4 years ago
butyoutoldmeiwasfunny reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 phir-milenge liked this · 4 years ago
phir-milenge liked this · 4 years ago -
 androgynousscissorspsychicbear liked this · 4 years ago
androgynousscissorspsychicbear liked this · 4 years ago -
 ct2311 liked this · 4 years ago
ct2311 liked this · 4 years ago -
 ajime64 liked this · 4 years ago
ajime64 liked this · 4 years ago -
 hey-there-xo liked this · 4 years ago
hey-there-xo liked this · 4 years ago -
 1e4tfss liked this · 4 years ago
1e4tfss liked this · 4 years ago -
 mybrainlacksharmonics reblogged this · 4 years ago
mybrainlacksharmonics reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 espedro liked this · 4 years ago
espedro liked this · 4 years ago -
 dmh3000 reblogged this · 4 years ago
dmh3000 reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 katherinebly liked this · 4 years ago
katherinebly liked this · 4 years ago -
 rou-uor liked this · 4 years ago
rou-uor liked this · 4 years ago -
 choppedtigerllama liked this · 4 years ago
choppedtigerllama liked this · 4 years ago -
 spilloverlove liked this · 4 years ago
spilloverlove liked this · 4 years ago -
 enbylvania65000 liked this · 4 years ago
enbylvania65000 liked this · 4 years ago -
 x2004f liked this · 4 years ago
x2004f liked this · 4 years ago -
 otakuandwriterlover liked this · 4 years ago
otakuandwriterlover liked this · 4 years ago -
 passamontanhas liked this · 4 years ago
passamontanhas liked this · 4 years ago
Explore the universe and discover our home planet with the official NASA Tumblr account
1K posts