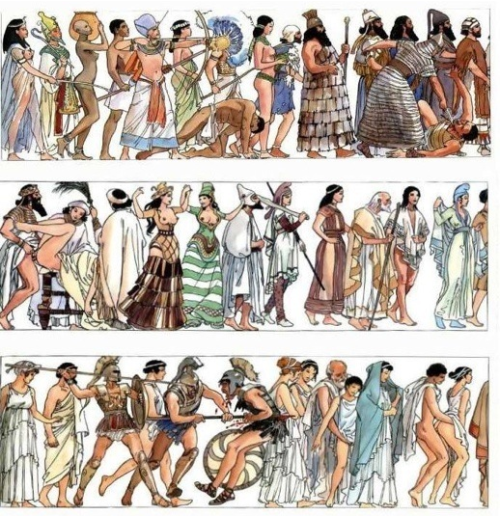
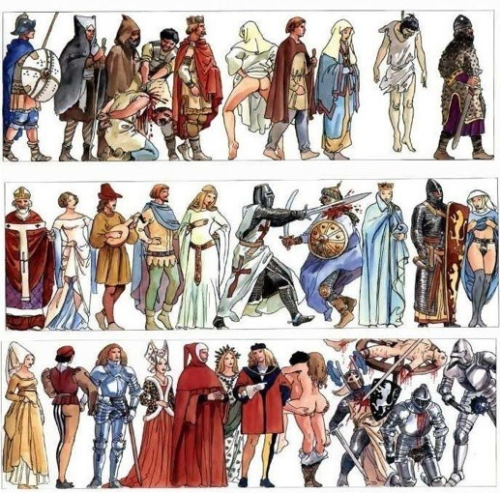
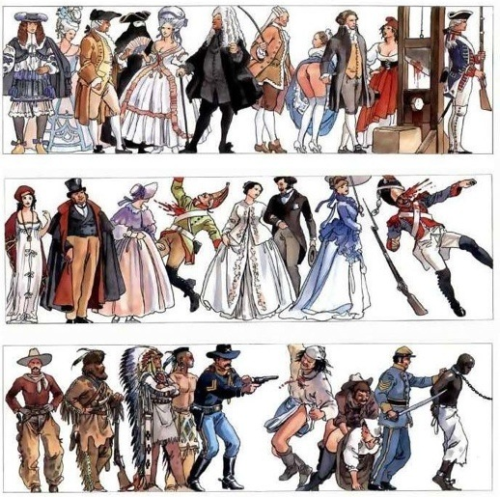
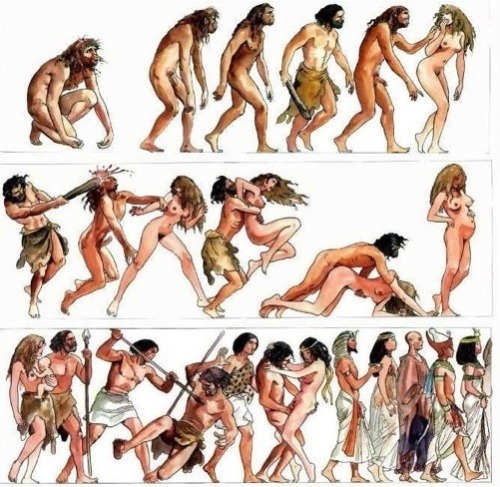
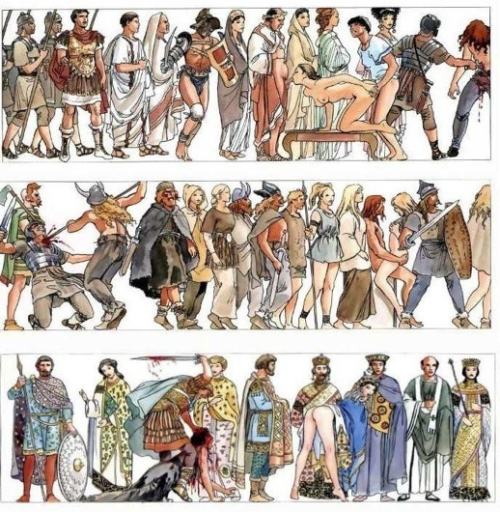
At What Point In History Do You Think Americans Stopped Having British Accents
at what point in history do you think americans stopped having british accents
More Posts from Fibonaccite and Others

I decided to create a masterpost that would help you with what you are struggling with. Hopefully any of the links below will help you! Reminder; You’re going to be okay. What you are going through will pass, just remember to breathe.
————————————————————————————-
Distractions;
Here are some distractions to help keep your mind occupied so you aren’t too focused on your thoughts.
-Draw something
-This website translates the time into colours.
-Create your own galaxy.
-Play flowing.
-Make a 3D line travel where ever you like.
-Listen to music.
-Calm.
-Ocean mood, do nothing for two minutes.
Sleep issues;
- 8 hour sleep music.
-Rainy mood.
-Meditation.
-Coping with nightmares.
-How to cope with nightmares, 11 steps.
-Calm
-Foods that can affect your sleeping, both positive and negatively.
Uncomfortable with silence;
-Rainy mood.
-10 hours of rain and thunder.
-3 hours of rain and thunder.
-Human heartbeat.
-Rainforest.
-Sound of rain on a tin roof.
-Autumn wind.
-Rain on a tent
-Traffic in the rain.
-Soft traffic.
-Fan.
-Train.
-Simply noise.
-My noise.
-Rainy cafe.
Anxiety;
-How to stop worrying.
-Tips to manage anxiety and stress.
-The 10 best ever anxiety management techniques.
-Self-help strategies for anxiety.
-Helping a friend with anxiety.
-All about worrying.
-8 myths about anxiety.
Sad, angry and depressed/depression;
-“I’m always sad”
-Feeling sad.
-Going through trauma.
-“I’m always angry”.
-Anger management.
-All about anger.
-National helplines and websites.
-Self-help strategies for depression.
-Dealing with depression at work.
-Dealing with depression at school.
Isolation and loneliness;
-Pets and mental health.
-All about loneliness.
-“I feel so alone”
-10 more ideas to help with loneliness.
-How to deal with loneliness.
Self-harm;
-Alternatives to self-harm and distraction techniques.
-146 things to do besides self-harm.
-More alternatives to self-harm.
-Self-harm alternatives.
-How to take care of self-harm wounds/injuries.
-Getting rid of scars.
Addiction;
-How to help a friend with a drug addiction.
-What is addiction?
-All about alcohol and addiction.
-The facts about drug addiction.
Eating disorders;
-Helping a friend with an eating disorder.
-Eating disorder treatments.
-Support services for eating disorders.
-Self-help tips with eating disorders.
-Eating disorder recovery.
-Recovering from an eating disorder.
-100+ reasons to recover.
-Understanding and managing eating disorders.
Dealing with self-hatred;
-3 ways to ease self-loathing.
-How to turn self-hatred into self-compassion.
-Self-hatred resources.
-10 step plan to deal with self-hate.
Suicidal;
-International suicide hotlines (1) (2)
-Preventing suicide.
-Reasons to stay alive.
-Dealing with suicidal thoughts and feelings.
-Coping with suicidal ideation.
Schizophrenia;
-All about schizophrenia.
-Helping a person with schizophrenia.
-Understanding and dealing with schizophrenia.
-Delusions and hallucinations.
OCD;
-Managing your OCD at home.
-Overcoming OCD.
-How to cope with OCD.
-Strategies for dealing with the anxious moments.
Borderline personality disorder;
-Helping someone with BPD.
-All about personality disorders.
-Treatment for BPD.
Abuse;
-Healthy relationships VS abusive relationships.
-Emotional abuse
-Overcoming sexual abuse.
-Hotlines services.
-5 ways to escape an abusive relationship.
-Domestic violence support.
-Signs of an abusive relationship.
-What do to if you’re in an abusive relationship.
-Surviving abuse.
-What you can do if you’re sexual harassed.
-Sexual assault support.
-What to do if you’ve been sexually assaulted or abused.
Bullying;
-How to stand up against bullying.
-How to protect yourself when it comes to cyber bullying.
-How to help stop people bullying you.
Loss and grief;
-How to cope with a suicide of a loved one.
-Grieving for a stranger.
-Common reactions to death.
-Working through grief.
(Other loss and grief)
-Moving away from friends and family.
-Coping with a breakup.
Getting help;
-Seeking help early.
-All about psychological treatments.
-Types of help.
-All about age and confidentiality.
Things you need to remember;
- Don’t stress about being fixed because you’re not broken.
-Remember to remind yourself of your accomplishments. Tell yourself that you’re proud of yourself, even if you’re not.
- This is temporary. You won’t always feel like this.
-You are not alone.
-You are enough.
-You are important.
-You are worth it.
-You are strong.
-You are not a failure,
-Good people exist.
-Reaching out shows strength.
-Breathe.
-Don’t listen to the thoughts that are not helping you.
-Give yourself credit.
-Don’t be ashamed of your emotions, for the good or bad ones.
-Treat yourself the same way as you would treat a good friend.
-Focus on the things you can change.
-Let go of toxic people.
-You don’t need to hide, you’re allowed to feel the way you do.
-Try not to beat yourself up.
-Something is always happening, you don’t want to miss out on what’s going to happen next.
-You are not a bother.
-Your existence is more than your appearance.
-You are smart.
-You are loved.
-You are wanted.
-You are needed.
-Better days are coming.
-Just because your past is dark, doesn’t mean your future isn’t bright.
-You have more potential than you think.
- Your value doesn’t decrease based on someone’s inability to see your worth.
Please remember to look after yourself and know that you are more than worth it and you deserve to be happy. Keep smiling butterflies x
job interviewer: what would you describe as your biggest weakness?
me: oh fake relationship au for sure



Icebergs are formed when large blocks of ice breaks off from glaciers ice shelf and is floating in open water. Because glaciers are built up from snow falling on the Antarctic continent over millennia, this ice consists of pure fresh water. This floating chunk of freshwater ice then interacts with seawater beneath them it.
As seawater is drawn deep under the ice shelves by the oceanic currents, it becomes supercooled and freezes to the base of the ice shelf. Because this ice is formed from seawater that contains organic matter and minerals it causes variety of colour and texture to the iceberg. As the bergs become fragmented and sculpted by the wind and waves, the different coloured layers can develop striking patterns.
Striped icebergs in a variety of colours, including brown, black, yellow, and blue has been spotted in freezing waters around Antarctica. (Source)
Why do we dream?

In the 3rd millennium BCE, Mesopotamian kings recorded and interpreted their dreams on wax tablets. In the years since, we haven’t paused in our quest to understand why we dream. And while we still don’t have any definitive answers, we have some theories. Here are seven reasons we might dream.

1. In the early 1900’s, Sigmund Freud proposed that while all of our dreams, including our nightmares, are a collection of images from our daily conscious lives, they also have symbolic meanings which relate to the fulfillment of our subconscious wishes. Freud theorized that everything we remember when we wake up from a dream is a symbolic representation of our unconscious, primitive thoughts, urges and desires. Freud believed that by analyzing those remembered elements, the unconscious content would be revealed to our conscious mind, and psychological issues stemming from its repression could be addressed and resolved.

2. To increase performance on certain mental tasks, sleep is good, but dreaming while sleeping is better. In 2010, researchers found that subjects were much better at getting through a complex 3D maze if they had napped and dreamed of the maze prior to their second attempt. In fact, they were up to ten times better at it than those who only thought of the maze while awake between attempts, and those who napped but did not dream about the maze. Researchers theorize that certain memory processes can happen only when we are asleep, and our dreams are a signal that these processes are taking place.

3. There are about ten thousand trillion neural connections within the architecture of your brain. They are created by everything you think, and everything you do. A 1983 neurobiological theory of dreaming, called “reverse learning,” holds that while sleeping, and mainly during REM sleep cycles, your neocortex reviews these neural connections and dumps the unnecessary ones. Without this unlearning process, which results in your dreams, your brain could be overrun by useless connections, and parasitic thoughts could disrupt the necessary thinking you need to do while you’re awake.

4. The “Continual Activation Theory” proposes that your dreams result from your brain’s need to constantly consolidate and create long term memories in order to function properly. So when external input falls below a certain level, like when you’re asleep, your brain automatically triggers the generation of data from its memory storages, which appear to you in the form of the thoughts and feelings you experience in your dreams. In other words, your dreams might be a random screensaver your brain turns on so it doesn’t completely shut down.

5. Dreams involving dangerous and threatening situations are very common, and the Primitive Instinct Rehearsal Theory holds that the content of a dream is significant to its purpose. Whether it’s an anxiety filled night of being chased through the woods by a bear, or fighting off a ninja in a dark alley, these dreams allow you to practice your fight or flight instincts and keep them sharp and dependable, in case you’ll need them in real life. But it doesn’t always have to be unpleasant; for instance, dreams about your attractive neighbor could actually give your reproductive instinct some practice too.

6. Stress neurotransmitters in the brain are much less active during the REM stage of sleep, even during dreams of traumatic experiences, leading some researchers to theorize that one purpose of dreaming is to take the edge off painful experiences to allow for psychological healing. Reviewing traumatic events in your dreams with less mental stress may grant you a clearer perspective and an enhanced ability to process them in psychologically healthy ways. People with certain mood disorders and PTSD often have difficulty sleeping, leading some scientists to believe that lack of dreaming may be a contributing factor to their illnesses.

7. Unconstrained by reality and the rules of conventional logic, in your dreams your mind can create limitless scenarios to help you grasp problems and formulate solutions that you may not consider while awake. John Steinbeck called it “the Committee of Sleep” and research has demonstrated the effectiveness of dreaming on problem solving. It’s also how renowned chemist August Kekule discovered the structure of the benzene molecule, and it’s the reason that sometimes the best solution for a problem is to “sleep on it”.
And those are just a few of the more prominent theories. As technology increases our capability for understanding the brain, it’s possible that one day we will discover the definitive reason for them; but until that time arrives, we’ll just have to keep on dreaming.
From the TED-Ed Lesson Why do we dream? - Amy Adkins
Animation by @clamanne
-
 penumbra-the-unicorn liked this · 1 month ago
penumbra-the-unicorn liked this · 1 month ago -
 missadorable96 liked this · 1 month ago
missadorable96 liked this · 1 month ago -
 askprofessorx liked this · 1 month ago
askprofessorx liked this · 1 month ago -
 hyperfixual liked this · 2 months ago
hyperfixual liked this · 2 months ago -
 fangsartworkshop reblogged this · 3 months ago
fangsartworkshop reblogged this · 3 months ago -
 xxiiageparanoid liked this · 4 months ago
xxiiageparanoid liked this · 4 months ago -
 kiyosheep liked this · 4 months ago
kiyosheep liked this · 4 months ago -
 earththeplanet liked this · 5 months ago
earththeplanet liked this · 5 months ago -
 fantrash-and-mediocre-moe-isms reblogged this · 5 months ago
fantrash-and-mediocre-moe-isms reblogged this · 5 months ago -
 fantrash-and-mediocre-moe-isms liked this · 5 months ago
fantrash-and-mediocre-moe-isms liked this · 5 months ago -
 creationvoid liked this · 5 months ago
creationvoid liked this · 5 months ago -
 thelittlemort reblogged this · 5 months ago
thelittlemort reblogged this · 5 months ago -
 annita89v5a8zjh liked this · 6 months ago
annita89v5a8zjh liked this · 6 months ago -
 annatxu5w liked this · 6 months ago
annatxu5w liked this · 6 months ago -
 fablenaught reblogged this · 6 months ago
fablenaught reblogged this · 6 months ago -
 methodicalsage reblogged this · 6 months ago
methodicalsage reblogged this · 6 months ago -
 methodicalsage liked this · 6 months ago
methodicalsage liked this · 6 months ago -
 cat-and-cazio liked this · 7 months ago
cat-and-cazio liked this · 7 months ago -
 nirilla reblogged this · 7 months ago
nirilla reblogged this · 7 months ago -
 nirilla liked this · 7 months ago
nirilla liked this · 7 months ago -
 placebob liked this · 7 months ago
placebob liked this · 7 months ago -
 themarydragon reblogged this · 7 months ago
themarydragon reblogged this · 7 months ago -
 queenofperv reblogged this · 7 months ago
queenofperv reblogged this · 7 months ago -
 byler-endgayme reblogged this · 7 months ago
byler-endgayme reblogged this · 7 months ago -
 byler-endgayme liked this · 7 months ago
byler-endgayme liked this · 7 months ago -
 starrisoul liked this · 8 months ago
starrisoul liked this · 8 months ago -
 haveahearttinman reblogged this · 8 months ago
haveahearttinman reblogged this · 8 months ago -
 ghostdaartist liked this · 8 months ago
ghostdaartist liked this · 8 months ago -
 photosbyjaye reblogged this · 8 months ago
photosbyjaye reblogged this · 8 months ago -
 squeackygee reblogged this · 8 months ago
squeackygee reblogged this · 8 months ago -
 crucified-dustymole reblogged this · 8 months ago
crucified-dustymole reblogged this · 8 months ago -
 ineffable-shenanigans reblogged this · 9 months ago
ineffable-shenanigans reblogged this · 9 months ago -
 annballofyarn liked this · 9 months ago
annballofyarn liked this · 9 months ago -
 twixpie liked this · 9 months ago
twixpie liked this · 9 months ago -
 carrythatwayt reblogged this · 9 months ago
carrythatwayt reblogged this · 9 months ago -
 carrythatwayt liked this · 9 months ago
carrythatwayt liked this · 9 months ago -
 blackmoonofthevoid reblogged this · 9 months ago
blackmoonofthevoid reblogged this · 9 months ago -
 blackmoonofthevoid liked this · 9 months ago
blackmoonofthevoid liked this · 9 months ago -
 manga-wolfsengel reblogged this · 9 months ago
manga-wolfsengel reblogged this · 9 months ago